Charting the Course: Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2025
Charting the Course: Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Course: Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Course: Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2025
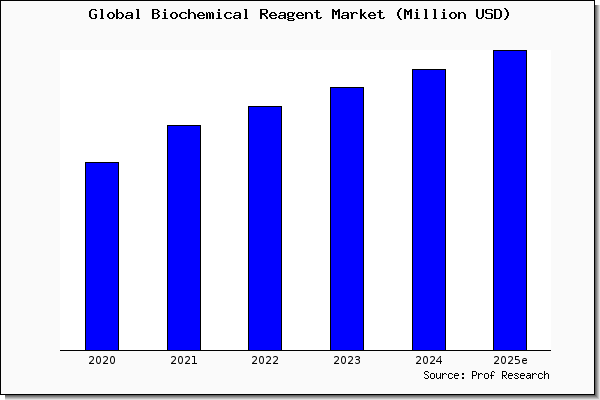
The field of biochemical sciences is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, groundbreaking discoveries, and a growing understanding of the intricate mechanisms governing life. As we look towards 2025, several key trends are poised to shape the future of this dynamic field.
1. Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to the Individual
The era of one-size-fits-all medicine is fading. Personalized medicine harnesses the power of genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, metabolic profile, and disease progression. This approach promises to revolutionize healthcare by:
- Increasing treatment efficacy: By identifying specific genetic markers associated with disease susceptibility and response to therapies, personalized medicine allows for more targeted and effective treatments.
- Reducing adverse drug reactions: Through individualized drug selection and dosage, the risk of side effects can be minimized, improving patient safety and well-being.
- Enabling early disease detection: By analyzing biomarkers in blood or other bodily fluids, personalized medicine can identify potential health risks early, allowing for timely intervention and prevention.
2. Synthetic Biology: Engineering Life for a Better Future
Synthetic biology is a rapidly developing field that aims to design and engineer biological systems for various applications. This involves manipulating genes, proteins, and metabolic pathways to create new functionalities and solve real-world problems. Some key areas of focus include:
- Biofuel production: Engineering microorganisms to efficiently produce biofuels from renewable resources can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
- Bioremediation: Synthetic biology can be used to develop organisms that can break down pollutants and clean up contaminated environments.
- Drug discovery and development: Engineering cells to produce new drugs and therapeutic proteins can accelerate drug discovery and provide novel treatments for diseases.
3. CRISPR-Cas9: A Powerful Tool for Genome Editing
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene editing technology that allows scientists to precisely target and modify specific DNA sequences. This tool has opened up unprecedented possibilities for:
- Disease treatment: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to correct genetic defects responsible for inherited diseases, offering hope for cures for conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease.
- Agricultural biotechnology: CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to improve crop yields, enhance nutritional content, and develop pest-resistant strains.
- Research and development: CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful tool for studying gene function and understanding the mechanisms underlying disease development.
4. Artificial Intelligence in Biochemical Sciences
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming biochemical sciences, enabling researchers to analyze vast datasets, predict protein structures, and develop new drugs with unprecedented speed and accuracy. Key applications of AI in biochemistry include:
- Drug discovery and development: AI algorithms can analyze large datasets of chemical structures and biological activity to identify potential drug candidates and optimize their properties.
- Protein structure prediction: AI-powered tools can predict the three-dimensional structures of proteins, providing insights into their function and interactions with other molecules.
- Metabolic pathway analysis: AI can be used to analyze complex metabolic networks and identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
5. Microbiome Research: Understanding the Microbial World Within
The microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms that inhabit our bodies, playing crucial roles in digestion, immunity, and overall health. Research into the microbiome is revealing its profound impact on human health and disease, leading to:
- Personalized microbiome therapies: Understanding the unique composition and function of each individual’s microbiome allows for tailored interventions to restore microbial balance and treat conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and obesity.
- Probiotics and prebiotics: These dietary supplements can modulate the microbiome composition and promote gut health, leading to improvements in digestion, immunity, and mental well-being.
- Development of new diagnostic tools: By analyzing the microbiome, researchers are developing new diagnostic tools for early detection of diseases like cancer and inflammatory bowel disease.
6. Metabolomics: Unraveling the Metabolic Landscape
Metabolomics is the study of all the small molecules (metabolites) present in an organism or cell. This field provides a snapshot of the metabolic state of a system, offering valuable insights into:
- Disease diagnosis and monitoring: Metabolomics can identify biomarkers associated with specific diseases and monitor treatment response.
- Drug discovery and development: By analyzing metabolic changes in response to drug treatment, researchers can identify potential drug targets and assess drug efficacy.
- Nutritional research: Metabolomics can be used to study the effects of different diets on metabolic health and identify potential nutritional interventions.
7. Proteomics: Studying the Proteome in Detail
Proteomics focuses on studying the complete set of proteins (proteome) in a cell or organism. This field provides insights into protein function, interactions, and modifications, offering a comprehensive understanding of biological processes. Key applications of proteomics include:
- Disease biomarker discovery: Proteomics can identify proteins that are differentially expressed in diseased cells, providing potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and monitoring.
- Drug target identification: Proteomics can identify proteins that are involved in disease pathways and could be targeted by new drugs.
- Understanding protein function: Proteomics provides valuable information about protein interactions, modifications, and localization, shedding light on their roles in biological processes.
8. Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering: Building the Future of Medicine
Biomaterials are materials that interact with biological systems, while tissue engineering aims to create functional tissues and organs for transplantation. These fields are converging to develop innovative solutions for:
- Tissue regeneration: Biomaterials and tissue engineering techniques are being used to develop scaffolds that support the growth and repair of damaged tissues, offering new treatments for injuries and diseases.
- Organ transplantation: Bioprinting and tissue engineering techniques are paving the way for creating functional organs for transplantation, addressing the critical shortage of organ donors.
- Drug delivery systems: Biomaterials can be used to develop controlled-release drug delivery systems, improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects.
Related Searches:
1. Advances in Biotechnology: This encompasses the broader landscape of advancements in biotechnology, including genetic engineering, bioinformatics, and synthetic biology, with a focus on their impact on healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability.
2. Future of Healthcare: This explores the future of healthcare, considering the impact of emerging technologies like AI, personalized medicine, and gene editing on disease prevention, treatment, and patient care.
3. Genomics and Personalized Medicine: This delves deeper into the role of genomics in personalized medicine, examining how genetic information can be used to tailor treatments, predict disease risk, and guide preventive measures.
4. Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering Applications: This explores specific applications of biomaterials and tissue engineering, focusing on their potential to address challenges in wound healing, bone regeneration, and organ transplantation.
5. Ethical Implications of Biotechnology: This examines the ethical considerations surrounding the use of biotechnology, including issues related to gene editing, synthetic biology, and the potential for genetic discrimination.
6. Nanotechnology in Biochemical Sciences: This explores the role of nanotechnology in biochemical sciences, highlighting its applications in drug delivery, diagnostics, and bioimaging.
7. Bioinformatics and Big Data Analysis: This focuses on the use of bioinformatics tools and techniques for analyzing large datasets in biochemical sciences, including genomic data, proteomic data, and metabolomic data.
8. Trends in Biopharmaceutical Industry: This examines the trends in the biopharmaceutical industry, focusing on the development of new drugs, therapies, and diagnostic tools, as well as the impact of emerging technologies on the industry.
FAQs:
1. What are the key challenges facing biochemical sciences in 2025?
- Ethical considerations: The development of powerful technologies like gene editing and synthetic biology raises ethical concerns about their potential misuse and impact on society.
- Data management and analysis: The increasing volume of data generated in biochemical sciences poses challenges for storage, analysis, and interpretation.
- Public perception and acceptance: Public understanding and acceptance of new technologies, particularly those related to genetic engineering and synthetic biology, are crucial for their successful implementation.
2. How will trends in biochemical sciences impact the future of healthcare?
- Improved disease prevention and early detection: Personalized medicine and advanced diagnostic tools will enable earlier identification of disease risks and facilitate proactive interventions.
- More effective and targeted treatments: Personalized therapies tailored to individual genetic profiles and disease characteristics will enhance treatment efficacy and minimize side effects.
- Development of novel therapies: Gene editing, synthetic biology, and other emerging technologies will pave the way for new treatments for previously untreatable diseases.
3. What are the potential benefits of personalized medicine?
- Increased treatment efficacy: By targeting treatments to individual genetic profiles and disease characteristics, personalized medicine can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
- Reduced adverse drug reactions: By selecting appropriate drugs and dosages based on individual genetic makeup, personalized medicine can minimize the risk of side effects.
- Enhanced patient safety and well-being: Personalized medicine empowers patients to take a more active role in managing their health, leading to improved outcomes and overall well-being.
4. How will AI impact the field of biochemistry?
- Accelerated drug discovery and development: AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of chemical structures and biological activity, identifying potential drug candidates and optimizing their properties.
- Improved protein structure prediction: AI-powered tools can predict the three-dimensional structures of proteins, providing insights into their function and interactions with other molecules.
- Enhanced metabolic pathway analysis: AI can be used to analyze complex metabolic networks and identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
5. What are the implications of microbiome research for human health?
- Personalized microbiome therapies: Understanding the unique composition and function of each individual’s microbiome allows for tailored interventions to restore microbial balance and treat conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and obesity.
- Probiotics and prebiotics: These dietary supplements can modulate the microbiome composition and promote gut health, leading to improvements in digestion, immunity, and mental well-being.
- Development of new diagnostic tools: By analyzing the microbiome, researchers are developing new diagnostic tools for early detection of diseases like cancer and inflammatory bowel disease.
Tips:
- Stay informed about emerging technologies: Keep abreast of the latest advancements in gene editing, synthetic biology, AI, and other emerging technologies that are transforming biochemical sciences.
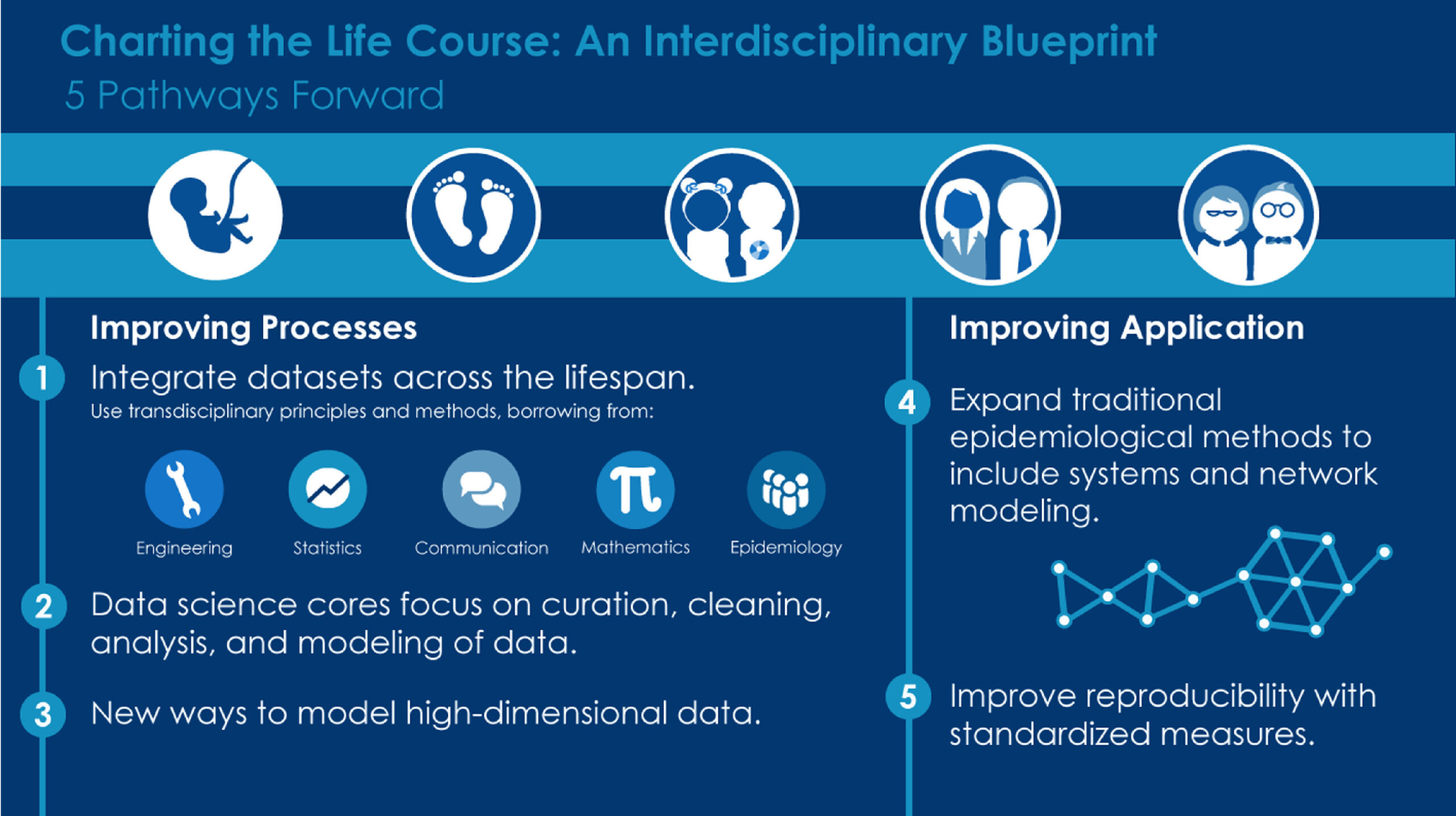
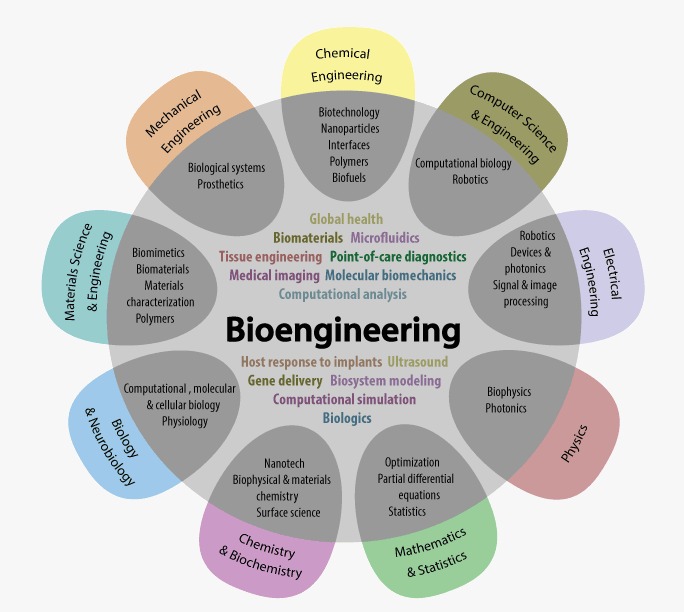
- Embrace interdisciplinary collaboration: Collaboration across disciplines, including biology, chemistry, computer science, and medicine, is essential for addressing complex challenges in biochemical sciences.
- Foster ethical awareness: Be mindful of the ethical considerations surrounding the use of powerful technologies like gene editing and synthetic biology, and advocate for responsible research and development practices.
- Develop critical thinking skills: Be able to evaluate scientific evidence, distinguish between reliable and unreliable information, and formulate informed opinions on emerging trends in biochemical sciences.
Conclusion:
The trends in biochemical sciences 2025 hold immense promise for addressing global challenges in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability. Personalized medicine, synthetic biology, gene editing, and AI are poised to revolutionize our understanding of life and pave the way for new treatments, diagnostics, and therapies. However, it is crucial to navigate these advancements with ethical awareness and responsible research practices, ensuring that these innovations benefit humanity and contribute to a brighter future.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)



/periodictrendstable-5c4a46614cedfd000187c5db.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Course: Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!