Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping 2025
Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping 2025
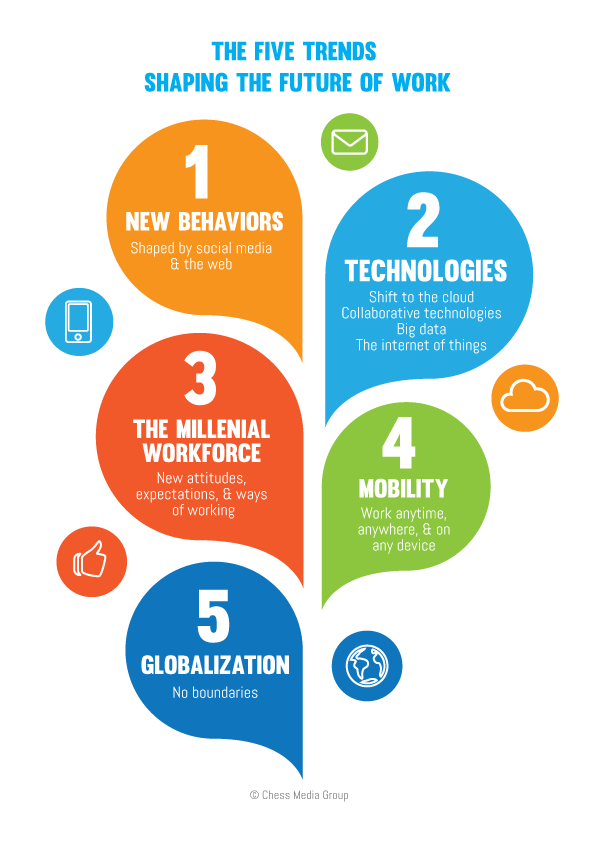
The world is in a constant state of flux, driven by technological advancements, societal shifts, and evolving consumer behaviors. As we approach 2025, understanding the trends that will shape our future is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. This comprehensive analysis explores eight key trends that will significantly impact various aspects of our lives, offering insights into their potential benefits, implications, and strategies for navigating this evolving landscape.
1. The Rise of the Metaverse
The metaverse is a collective term for persistent, shared, 3D virtual spaces accessible through various devices, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. It promises a future where individuals can work, socialize, learn, and play in immersive, interactive environments.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Social Interaction: The metaverse offers a new platform for building communities, fostering relationships, and engaging in shared experiences.
- New Economic Opportunities: The metaverse creates opportunities for businesses to create virtual products and services, generate revenue through virtual transactions, and develop new business models.
- Transformative Education and Training: The metaverse provides immersive learning environments, allowing for personalized instruction, interactive simulations, and hands-on training in various fields.
Implications:
- Privacy and Security Concerns: The metaverse raises concerns about data privacy, user identity, and potential misuse of virtual spaces.
- Digital Divide: Access to the metaverse could exacerbate existing digital divides, with disparities in technology adoption and internet connectivity creating barriers to participation.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical dilemmas related to virtual identity, ownership, and the potential for manipulation require careful consideration.
2. The Exponential Growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and integrated into various aspects of our lives. From automating tasks and improving efficiency to revolutionizing healthcare and scientific discovery, AI is transforming industries and impacting our daily routines.
Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex and creative work.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and provide insights that can inform better decision-making.
- Personalized Experiences: AI can tailor experiences to individual preferences, offering personalized recommendations, customized services, and tailored content.
Implications:
- Job Displacement: The automation capabilities of AI raise concerns about job displacement and the need for reskilling and upskilling programs.
- Ethical Considerations: AI raises ethical concerns related to bias, fairness, transparency, and the potential for misuse.
- Data Privacy and Security: The reliance on data for AI applications emphasizes the importance of data privacy, security, and responsible data management.
3. The Advancements in Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
Biotechnology and genetic engineering are rapidly progressing, enabling new treatments for diseases, improving crop yields, and revolutionizing healthcare.
Benefits:
- Disease Prevention and Treatment: Advancements in biotechnology offer potential cures for currently incurable diseases and personalized medicine tailored to individual genetic profiles.
- Enhanced Food Security: Genetic engineering can improve crop yields, enhance nutritional value, and make crops more resistant to pests and diseases.
- Environmental Sustainability: Biotechnology can contribute to sustainable agriculture and biofuel production, reducing environmental impact.
Implications:
- Ethical Concerns: Genetic engineering raises ethical questions about human enhancement, designer babies, and the potential for unintended consequences.
- Social Equity: Access to genetic technologies could create disparities in healthcare and exacerbate existing inequalities.
- Regulation and Oversight: The rapid pace of advancements requires robust regulatory frameworks to ensure responsible research and development.
4. The Rise of the Sharing Economy
The sharing economy involves the sharing of resources, assets, and services through peer-to-peer platforms, fostering collaborative consumption and reducing the need for individual ownership.
Benefits:
- Increased Access and Affordability: The sharing economy provides access to goods and services that may be expensive or unavailable through traditional means.
- Sustainable Consumption: Sharing resources reduces waste, promotes resource efficiency, and minimizes environmental impact.
- Community Building: The sharing economy fosters a sense of community and collaboration, connecting individuals through shared interests and needs.
Implications:
- Regulation and Legality: The sharing economy requires clear legal frameworks and regulations to address issues such as liability, insurance, and consumer protection.
- Competition with Traditional Industries: The sharing economy poses challenges to traditional industries, such as transportation, hospitality, and retail.
- Labor Standards and Worker Rights: The sharing economy raises questions about labor standards, worker rights, and the need for adequate compensation and benefits.
5. The Growing Importance of Sustainability and Climate Action
Sustainability and climate action are increasingly critical as the world faces the challenges of climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation.
Benefits:
- Environmental Protection: Sustainable practices help preserve natural resources, reduce pollution, and mitigate climate change.
- Economic Growth: Sustainable businesses are often more resilient, innovative, and create long-term value.
- Social Equity: Sustainable development aims to promote social equity and improve quality of life for all.
Implications:
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products and services, driving businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Policy and Regulation: Governments are implementing policies and regulations to promote sustainability and reduce environmental impact.
- Innovation and Technology: Sustainable solutions require innovative technologies and advancements in areas such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and waste management.
6. The Transformation of Work and the Future of Labor
The future of work is being reshaped by technological advancements, automation, and changing workforce demographics. This shift requires individuals and organizations to adapt to new skills, work models, and career paths.
Benefits:
- Increased Flexibility and Autonomy: The future of work offers greater flexibility, remote work opportunities, and the potential for greater autonomy.
- Enhanced Creativity and Innovation: Technology can augment human capabilities, enabling employees to focus on more creative and strategic tasks.
- Lifelong Learning: The future of work demands continuous learning and adaptability, encouraging individuals to develop new skills and knowledge throughout their careers.
Implications:
- Job Displacement and Reskilling: Automation and technological advancements may displace certain jobs, requiring individuals to acquire new skills and adapt to evolving job markets.
- Workforce Diversity and Inclusion: The future of work presents an opportunity to create more inclusive and diverse work environments.
- Work-Life Balance: The rise of remote work and flexible schedules can enhance work-life balance, but also requires careful consideration of potential challenges.
7. The Rise of Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision making is becoming increasingly important as organizations leverage data analytics and insights to improve efficiency, optimize operations, and make informed decisions.
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Data analysis can identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and improve resource allocation.
- Enhanced Customer Understanding: Data insights can provide a deeper understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and needs, enabling businesses to personalize offerings and improve customer satisfaction.
- Competitive Advantage: Data-driven decision making can provide a competitive advantage by enabling organizations to anticipate trends, identify opportunities, and respond quickly to market changes.
Implications:
- Data Privacy and Security: The reliance on data for decision making emphasizes the importance of data privacy, security, and responsible data management.
- Data Literacy: The increasing use of data requires individuals and organizations to develop data literacy skills to interpret and utilize data effectively.
- Ethical Considerations: Data-driven decision making raises ethical concerns about bias, fairness, transparency, and the potential for misuse.
8. The Growing Importance of Personalization and Customization
Personalization and customization are becoming increasingly important as consumers demand tailored experiences and products that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Benefits:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Personalized experiences and customized products can enhance customer satisfaction by providing a more relevant and engaging experience.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Personalized offerings can foster stronger customer relationships and increase customer loyalty.
- Enhanced Revenue Growth: Personalized products and services can drive revenue growth by catering to individual preferences and needs.
Implications:
- Data Privacy and Security: The collection and use of data for personalization raises concerns about data privacy, security, and the potential for misuse.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Implementing personalization and customization requires sophisticated technology and infrastructure.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations surrounding data collection, transparency, and the potential for bias require careful attention.
Related Searches
- Future Trends 2025: This search explores broader predictions about the future, encompassing various sectors and aspects of society.
- Technology Trends 2025: This search focuses on specific technological advancements and their impact on various industries.
- Business Trends 2025: This search examines trends relevant to businesses, including innovation, disruption, and emerging business models.
- Social Trends 2025: This search analyzes societal shifts, demographic changes, and evolving consumer behaviors.
- Economic Trends 2025: This search explores economic forecasts, market conditions, and potential economic disruptions.
- Environmental Trends 2025: This search focuses on environmental issues, climate change, sustainability, and resource management.
- Healthcare Trends 2025: This search examines advancements in healthcare, including personalized medicine, biotechnology, and digital health.
- Education Trends 2025: This search explores trends in education, including online learning, personalized instruction, and the changing role of teachers.
FAQs
-
What are the biggest challenges we face in 2025?
The biggest challenges in 2025 include climate change, economic inequality, technological disruption, and the need for responsible AI development. -
How can we prepare for the future?
Individuals can prepare by acquiring new skills, embracing lifelong learning, and staying informed about emerging trends. Businesses can adapt by fostering innovation, embracing digital transformation, and prioritizing sustainability. -
Will technology make our lives easier or harder?
Technology has the potential to make our lives easier by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and providing access to information. However, it also presents challenges related to job displacement, ethical considerations, and data privacy. -
What are the ethical implications of these trends?
These trends raise ethical concerns about privacy, bias, fairness, and the potential for misuse of technology. It is crucial to develop ethical frameworks and regulations to ensure responsible development and application of these technologies. -
How can we ensure a sustainable future?
A sustainable future requires collective action from individuals, businesses, and governments. This includes adopting sustainable practices, investing in renewable energy, reducing waste, and promoting responsible consumption.
Tips
- Stay Informed: Continuously update your knowledge about emerging trends and technologies.
- Embrace Lifelong Learning: Develop new skills and adapt to changing job markets.
- Foster Innovation: Encourage creativity and explore new ideas to stay ahead of the curve.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Adopt sustainable practices and support businesses committed to environmental responsibility.
- Embrace Collaboration: Collaborate with others to address complex challenges and find innovative solutions.
Conclusion
The trends shaping 2025 present both opportunities and challenges. By understanding these trends and embracing a forward-thinking approach, individuals, businesses, and governments can navigate this evolving landscape and create a more equitable, sustainable, and prosperous future. The key lies in embracing innovation, prioritizing ethical considerations, and fostering collaboration to build a future that benefits all.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!