Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work
Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Hybrid Work Models
- 3.2 2. The Growing Importance of Digital Collaboration Tools
- 3.3 3. The Rise of the Gig Economy and Freelancing
- 3.4 4. The Growing Importance of Upskilling and Reskilling
- 3.5 5. The Importance of Employee Well-being and Mental Health
- 3.6 6. The Impact of Remote Work on Diversity and Inclusion
- 3.7 7. The Future of Remote Work Legislation and Regulations
- 3.8 8. The Environmental Impact of Remote Work
- 4 FAQs About Remote Working Trends 2025-2026
- 5 Tips for Navigating Remote Working Trends 2025-2026
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Closure
Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work
The COVID-19 pandemic ushered in a dramatic shift in the way we work, accelerating the adoption of remote work practices globally. While the initial transition was driven by necessity, the long-term impact has been profound, reshaping the landscape of employment and ushering in a new era of flexible work arrangements. As we move towards 2025 and 2026, the trajectory of remote working trends continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changing workforce demographics, and evolving business needs. This comprehensive analysis explores the key trends shaping the future of work, highlighting their implications for individuals, businesses, and the global economy.
1. The Rise of Hybrid Work Models
The rigid boundaries between traditional office work and fully remote arrangements are blurring, giving rise to hybrid work models. These models offer employees the flexibility to work from home, the office, or a combination of both, based on individual needs and project demands. This approach fosters a more balanced work-life integration, promoting employee well-being while maintaining a sense of community and collaboration within the workplace.
Benefits of Hybrid Work Models:
- Increased Flexibility: Employees enjoy greater control over their work schedules and locations, enabling them to better manage personal commitments and work-life balance.
- Enhanced Productivity: Studies have shown that hybrid workers often report higher levels of productivity due to reduced distractions and improved focus.
- Improved Employee Morale: The flexibility and autonomy offered by hybrid work arrangements contribute to higher employee morale and job satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: Companies can benefit from reduced office space requirements and associated expenses, leading to significant cost savings.
- Talent Acquisition: Hybrid work arrangements attract a broader pool of talent, including remote workers and individuals seeking flexible work arrangements.
Challenges of Hybrid Work Models:
- Maintaining Team Cohesion: Ensuring effective communication and collaboration between in-office and remote team members can be challenging.
- Managing Technology Infrastructure: Hybrid work models require robust IT infrastructure and support systems to facilitate seamless collaboration and data sharing.
- Work-Life Boundaries: Maintaining clear boundaries between work and personal life can be difficult for some employees, leading to burnout and stress.
Examples of Hybrid Work Models:
- Flexible Work Schedules: Employees can choose their work hours and days, allowing for greater flexibility and control.
- Remote-First with Office Days: Teams primarily work remotely but gather at the office for specific meetings, team-building events, or collaborative projects.
- Office-First with Remote Options: Employees primarily work from the office but have the option to work remotely on specific days or for specific tasks.
2. The Growing Importance of Digital Collaboration Tools
As remote work becomes increasingly prevalent, the need for robust digital collaboration tools becomes paramount. These tools facilitate seamless communication, information sharing, and project management, enabling teams to work effectively regardless of their physical location.
Types of Digital Collaboration Tools:
- Communication Platforms: Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom enable real-time communication, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Project Management Software: Platforms such as Asana, Trello, and Jira help teams organize tasks, track progress, and collaborate on projects.
- Cloud Storage and File Sharing: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive provide secure and accessible storage for documents, presentations, and other files.
- Virtual Whiteboards and Brainstorming Tools: Tools like Miro and Mural facilitate collaborative brainstorming, ideation, and visualization.
- Digital Document Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Google Docs, Microsoft Word Online, and Dropbox Paper enable real-time co-editing of documents.
Impact of Digital Collaboration Tools:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Digital tools break down geographical barriers, enabling seamless collaboration between team members in different locations.
- Improved Productivity: Real-time communication and task management features enhance productivity by streamlining workflows and reducing communication bottlenecks.
- Increased Accessibility: Digital tools make it easier for individuals with disabilities or those facing mobility challenges to participate in the workforce.
- Reduced Costs: Digital collaboration tools can reduce travel expenses, meeting room costs, and other traditional office expenses.
Challenges of Digital Collaboration Tools:
- Security Risks: Sharing sensitive information through digital platforms requires robust security measures to prevent data breaches.
- Technical Issues: Technical glitches and software compatibility issues can disrupt workflows and impact productivity.
- Digital Divide: Lack of access to reliable internet and digital devices can create disparities in participation and opportunities.
3. The Rise of the Gig Economy and Freelancing
The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, is expanding rapidly, driven by the flexibility and autonomy it offers both employers and employees. This trend is particularly relevant to remote work, as it enables individuals to access a global talent pool and build their own careers on their terms.
Benefits of the Gig Economy:
- Flexibility and Autonomy: Freelancers and gig workers enjoy greater control over their work schedules and projects, enabling them to build a career that aligns with their lifestyle and preferences.
- Access to Diverse Opportunities: The gig economy provides access to a wide range of projects and clients, allowing individuals to develop skills and build experience in various fields.
- Increased Income Potential: Freelancers and gig workers can set their own rates and potentially earn higher income compared to traditional employment.
- Reduced Overhead Costs: Gig workers often have lower overhead costs compared to traditional businesses, enabling them to retain a higher percentage of their earnings.
Challenges of the Gig Economy:
- Job Security: Gig work often lacks the stability and benefits associated with traditional employment, such as health insurance and paid time off.
- Income Volatility: Fluctuating project availability and unpredictable income can create financial instability for gig workers.
- Lack of Employer Benefits: Gig workers typically lack access to employer-sponsored benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid sick leave.
- Competition and Pricing Pressure: The highly competitive nature of the gig economy can lead to pricing pressure and difficulty securing high-paying projects.
Examples of Gig Economy Platforms:
- Freelancing Platforms: Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Guru connect freelancers with clients seeking various services.
- Ride-Sharing and Delivery Services: Platforms like Uber, Lyft, and DoorDash enable individuals to earn income by providing transportation or delivery services.
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Etsy and Amazon Handmade allow individuals to sell handmade goods and crafts.
4. The Growing Importance of Upskilling and Reskilling
The rapid pace of technological advancements and evolving job demands necessitate continuous upskilling and reskilling. Remote work, in particular, requires individuals to adapt to new technologies, learn new skills, and stay competitive in a global talent pool.
Importance of Upskilling and Reskilling:
- Staying Competitive: Upskilling and reskilling enable individuals to adapt to changing job requirements and remain competitive in the labor market.
- Career Advancement: Acquiring new skills and knowledge can lead to career advancement, increased earning potential, and greater job security.
- Adaptability and Innovation: Upskilling and reskilling foster adaptability and innovation, enabling individuals to embrace new technologies and contribute to organizational growth.
- Personal Growth: Continuous learning and skill development contribute to personal growth, intellectual stimulation, and a sense of accomplishment.
Resources for Upskilling and Reskilling:
- Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer a wide range of online courses and certifications in various fields.
- Corporate Training Programs: Many companies offer internal training programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
- Mentorship and Coaching: Mentorship and coaching programs can provide guidance, support, and practical advice for career development.
- Networking and Industry Events: Attending industry events and networking with professionals can provide valuable insights and opportunities for learning.
Challenges of Upskilling and Reskilling:
- Time Constraints: Balancing work, family, and personal life can make it challenging to dedicate time to upskilling and reskilling.
- Financial Costs: Online courses and training programs can be expensive, posing a financial barrier for some individuals.
- Lack of Motivation: Maintaining motivation and staying committed to a learning journey can be challenging, especially when facing competing priorities.
5. The Importance of Employee Well-being and Mental Health
The shift to remote work has brought both benefits and challenges to employee well-being. While remote work offers flexibility and autonomy, it can also lead to isolation, blurred work-life boundaries, and increased stress. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of prioritizing employee well-being and providing support systems to address these challenges.
Strategies for Promoting Employee Well-being in a Remote Work Environment:
- Regular Communication and Check-Ins: Frequent communication and check-ins with team members help foster a sense of connection and provide opportunities for feedback and support.
- Flexible Work Schedules: Offering flexible work hours and schedules allows employees to better manage personal commitments and work-life balance.
- Mental Health Resources: Providing access to mental health resources, such as employee assistance programs and virtual therapy, can help address stress, anxiety, and other mental health concerns.
- Ergonomics and Workspace Design: Encouraging employees to create comfortable and ergonomic workspaces can help prevent physical discomfort and promote well-being.
- Encouraging Breaks and Disconnection: Promoting regular breaks, time off, and disconnection from work can help employees recharge and prevent burnout.
Benefits of Prioritizing Employee Well-being:
- Improved Productivity: Happy and healthy employees are more productive and engaged in their work.
- Reduced Absenteeism and Turnover: A focus on employee well-being can lead to reduced absenteeism and turnover, contributing to a more stable workforce.
- Enhanced Company Culture: A positive and supportive work environment fosters a sense of community and belonging, contributing to a strong company culture.
- Stronger Employer Brand: Companies that prioritize employee well-being attract and retain top talent, enhancing their employer brand and reputation.
Challenges of Promoting Employee Well-being:
- Measuring and Tracking Impact: It can be challenging to measure and track the effectiveness of well-being initiatives.
- Resource Allocation: Implementing comprehensive well-being programs requires significant resource allocation, which may be a challenge for some companies.
- Cultural Resistance: Some organizations may resist embracing well-being initiatives due to cultural norms or perceived costs.
6. The Impact of Remote Work on Diversity and Inclusion
Remote work has the potential to promote diversity and inclusion in the workforce by breaking down geographical barriers and providing opportunities for individuals who may have previously faced limitations due to location or accessibility.
Benefits of Remote Work for Diversity and Inclusion:
- Expanded Talent Pool: Remote work allows companies to access a wider pool of talent, including individuals from diverse backgrounds, locations, and abilities.
- Reduced Bias: Remote work can reduce unconscious bias associated with traditional hiring practices, such as proximity and appearance.
- Flexibility for Diverse Needs: Remote work offers flexibility for individuals with diverse needs, such as caregivers, individuals with disabilities, or those seeking work-life balance.
- Enhanced Representation: By removing location barriers, remote work can lead to greater representation of diverse groups within organizations.
Challenges of Remote Work for Diversity and Inclusion:
- Digital Divide: Lack of access to reliable internet and digital devices can create disparities in participation and opportunities for individuals from underrepresented communities.
- Cultural Differences: Managing communication and collaboration across different cultures and time zones can be challenging.
- Social Isolation: Remote work can lead to social isolation, particularly for individuals from marginalized groups who may lack strong social networks.
- Lack of Mentorship and Networking Opportunities: Remote workers may have limited access to mentorship and networking opportunities, which can hinder career advancement.
Strategies for Promoting Diversity and Inclusion in a Remote Work Environment:
- Diversity and Inclusion Training: Providing training on diversity and inclusion best practices to all employees can help create a more inclusive workplace.
- Mentorship Programs: Establishing mentorship programs that connect remote workers with experienced colleagues can provide support and guidance.
- Virtual Networking Events: Organizing virtual networking events can help remote workers connect with colleagues and build relationships.
- Accessibility Tools and Support: Providing access to accessibility tools and support for individuals with disabilities can ensure equal participation and opportunities.
7. The Future of Remote Work Legislation and Regulations
As remote work becomes increasingly prevalent, governments and regulatory bodies are grappling with the legal and regulatory implications of this new model of work. This includes issues such as labor rights, taxation, and data privacy.
Key Areas of Remote Work Legislation and Regulation:
- Labor Laws: Governments are considering how to adapt existing labor laws to address issues such as minimum wage, overtime pay, and worker safety in a remote work context.
- Taxation: The rise of remote work has raised questions about tax residency, income tax obligations, and the allocation of tax revenue between different jurisdictions.
- Data Privacy: Remote work involves the transmission and storage of sensitive data, raising concerns about data security and privacy regulations.
- Workplace Safety: Governments are exploring how to ensure the safety and well-being of remote workers, including issues such as ergonomics, mental health, and workplace harassment.
Impact of Remote Work Legislation and Regulation:
- Clarity and Certainty: Clear and consistent legislation can provide clarity and certainty for both employers and employees, facilitating the smooth operation of remote work arrangements.
- Fairness and Equity: Regulations can ensure fair treatment and equal opportunities for all workers, regardless of their location or work arrangements.
- Protecting Worker Rights: Legislation can protect the rights of remote workers, such as their right to a living wage, safe working conditions, and access to benefits.
- Promoting Innovation and Growth: A supportive regulatory environment can foster innovation and growth in the remote work sector, creating new jobs and opportunities.
Challenges of Remote Work Legislation and Regulation:
- Harmonization of Laws: Achieving harmonization of remote work regulations across different jurisdictions can be challenging, leading to inconsistencies and complexities.
- Keeping Pace with Technological Advancements: Regulations need to be flexible and adaptable to keep pace with rapid technological advancements in the remote work sector.
- Balancing Worker Rights with Business Needs: Striking a balance between protecting worker rights and ensuring the competitiveness of businesses is a key challenge.
8. The Environmental Impact of Remote Work
Remote work has the potential to reduce the environmental impact associated with traditional office work, such as commuting emissions, office energy consumption, and waste generation.
Benefits of Remote Work for the Environment:
- Reduced Commuting Emissions: Remote work significantly reduces commuting emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Working from home can reduce energy consumption associated with office buildings, including heating, cooling, and lighting.
- Reduced Waste Generation: Remote work can lead to a reduction in office waste, such as paper, packaging, and food waste.
- Increased Use of Public Transportation: Some remote workers may choose to use public transportation for occasional commutes, further reducing emissions.
Challenges of Remote Work for the Environment:
- Increased Home Energy Consumption: Working from home can lead to increased energy consumption at home, especially if employees use multiple devices and appliances.
- E-Waste Generation: The increasing use of electronic devices for remote work can contribute to e-waste generation.
- Carbon Footprint of Technology: The production and use of technology for remote work have a carbon footprint, which needs to be considered.
- Digital Divide: Lack of access to reliable internet and digital devices can create disparities in participation and opportunities, potentially exacerbating environmental inequalities.
Strategies for Minimizing the Environmental Impact of Remote Work:
- Energy-Efficient Devices and Practices: Encourage employees to use energy-efficient devices, turn off lights and appliances when not in use, and adopt energy-saving practices.
- Remote Work Policies: Implement company policies that promote sustainable practices, such as encouraging employees to use public transportation or carpooling for occasional commutes.
- Recycling and Waste Reduction: Encourage employees to recycle and reduce waste at home, and provide resources for responsible disposal of electronic devices.
- Green Technology and Infrastructure: Invest in green technology and infrastructure, such as renewable energy sources and energy-efficient office spaces.
FAQs About Remote Working Trends 2025-2026
Q: Will remote work become the norm by 2025-2026?
A: While it is unlikely that all work will become fully remote, hybrid work models are expected to become increasingly prevalent. The future of work will likely involve a blend of remote, in-office, and flexible work arrangements, tailored to individual needs and company requirements.
Q: What are the biggest challenges to remote work adoption?
A: Some of the biggest challenges include maintaining team cohesion, managing technology infrastructure, ensuring work-life balance, and addressing the digital divide. Companies and individuals need to invest in appropriate technology, build strong communication channels, and prioritize employee well-being to overcome these challenges.
Q: How will remote work impact the real estate market?
A: The rise of remote work is expected to have a significant impact on the real estate market. Companies may reduce their office space requirements, leading to a shift in demand for commercial real estate. Residential real estate markets may see increased demand in suburban and rural areas, as remote workers seek more affordable and spacious living options.
Q: Will remote work lead to job losses?
A: While some jobs may be displaced due to automation or other factors, remote work is more likely to create new opportunities and reshape the job market rather than lead to widespread job losses. The shift to remote work will require individuals to adapt and acquire new skills, but it also opens up new avenues for entrepreneurship and freelance work.
Q: What are the ethical considerations surrounding remote work?
A: Ethical considerations include ensuring fair treatment and equal opportunities for all workers, regardless of their location, addressing potential biases in hiring and promotion, and protecting worker rights in a remote work context. Companies and governments need to establish clear ethical guidelines and frameworks to address these issues.
Q: How can individuals prepare for the future of remote work?
A: Individuals can prepare by developing essential skills such as digital literacy, communication, collaboration, and problem-solving. They can also invest in upskilling and reskilling opportunities, building a strong online presence, and networking with professionals in their field.
Tips for Navigating Remote Working Trends 2025-2026
- Embrace Flexibility: Be open to hybrid work models and flexible work arrangements, allowing for greater control over your work schedule and location.
- Invest in Technology: Ensure you have access to reliable internet, a comfortable and ergonomic workspace, and the necessary digital tools for effective communication and collaboration.
- Build Strong Communication Channels: Establish clear communication protocols with your team, utilize digital collaboration tools effectively, and participate actively in virtual meetings.
- Prioritize Well-being: Maintain a healthy work-life balance, take regular breaks, prioritize physical and mental health, and seek support when needed.
- Continuously Upskill and Reskill: Stay abreast of technological advancements and industry trends, invest in relevant training programs, and actively seek opportunities to develop new skills.
Conclusion
The *remote working trends



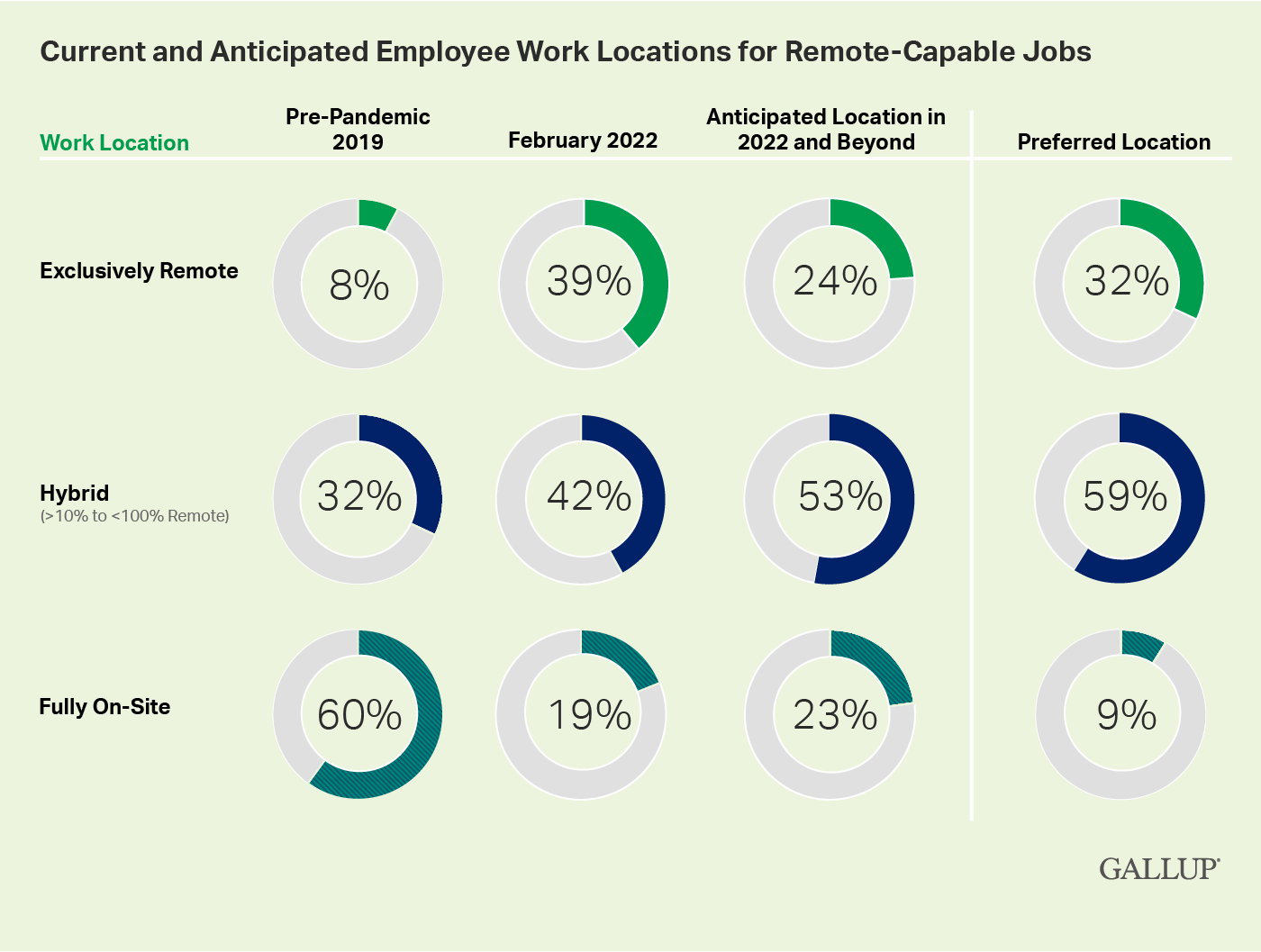
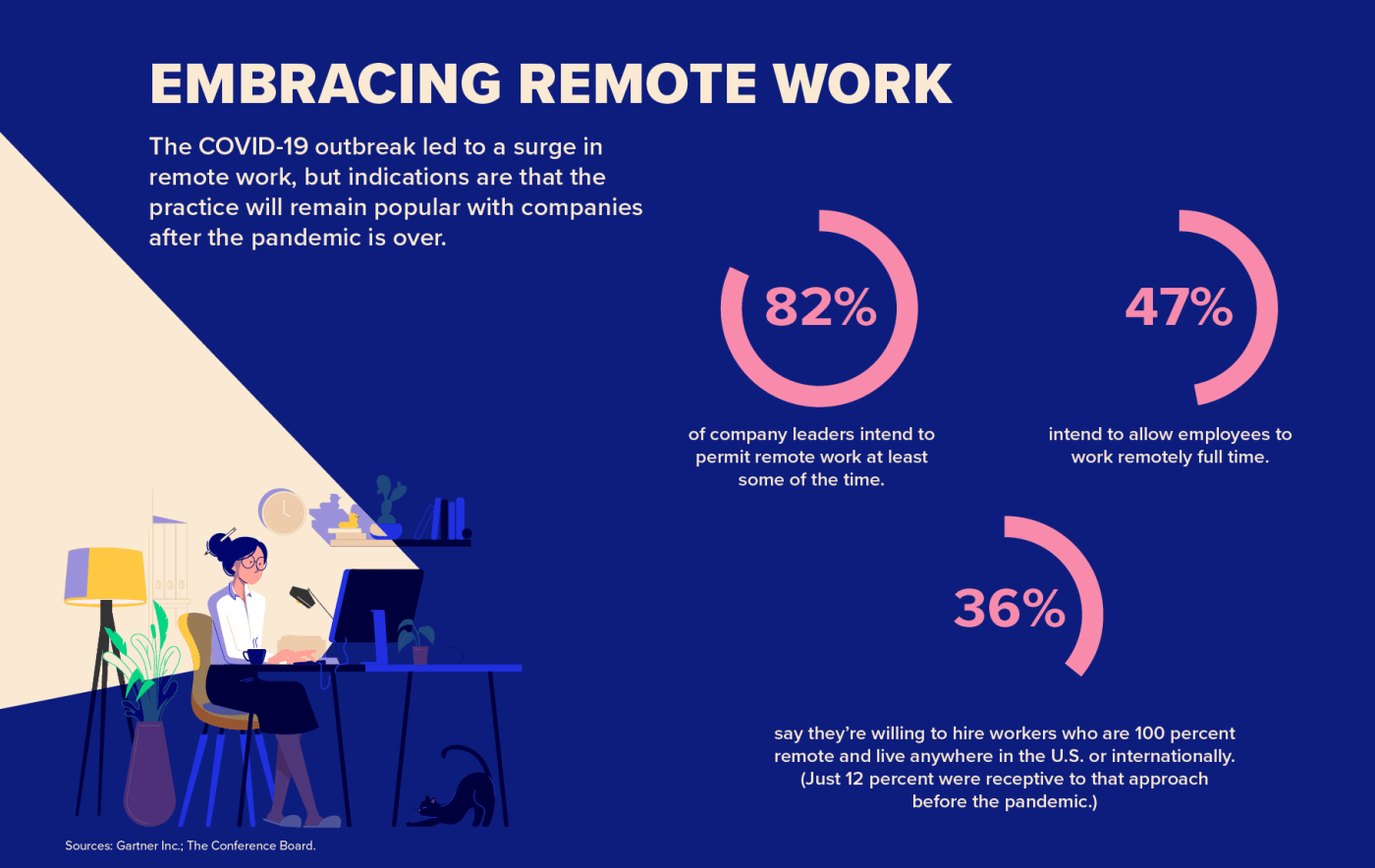
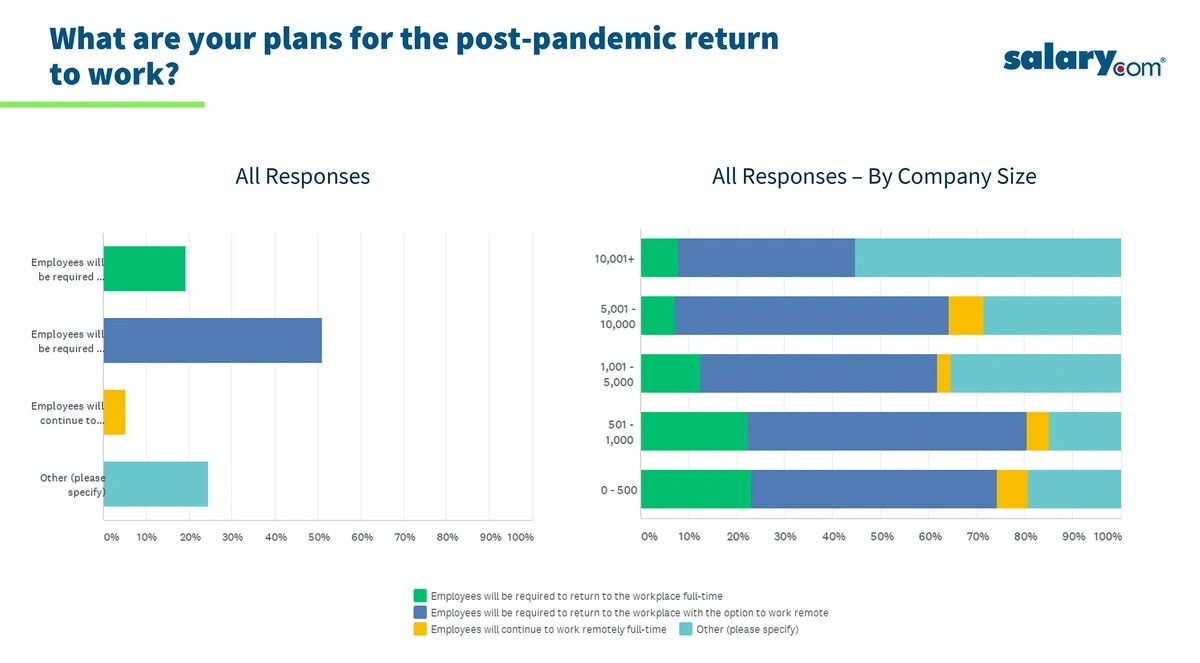
![25 Trending Remote Work Statistics [2023]: Facts, Trends, And](https://www.zippia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/36.2-million-americans-will-be-working-remotely.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Remote Working Trends 2025-2026: A Look into the Future of Work. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!