Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025
Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025
- 3.1 Construction Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Overview
- 3.2 Construction Trends 2025: Related Searches
- 3.3 Construction Trends 2025: FAQs
- 3.4 Construction Trends 2025: Tips
- 3.5 Construction Trends 2025: Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025
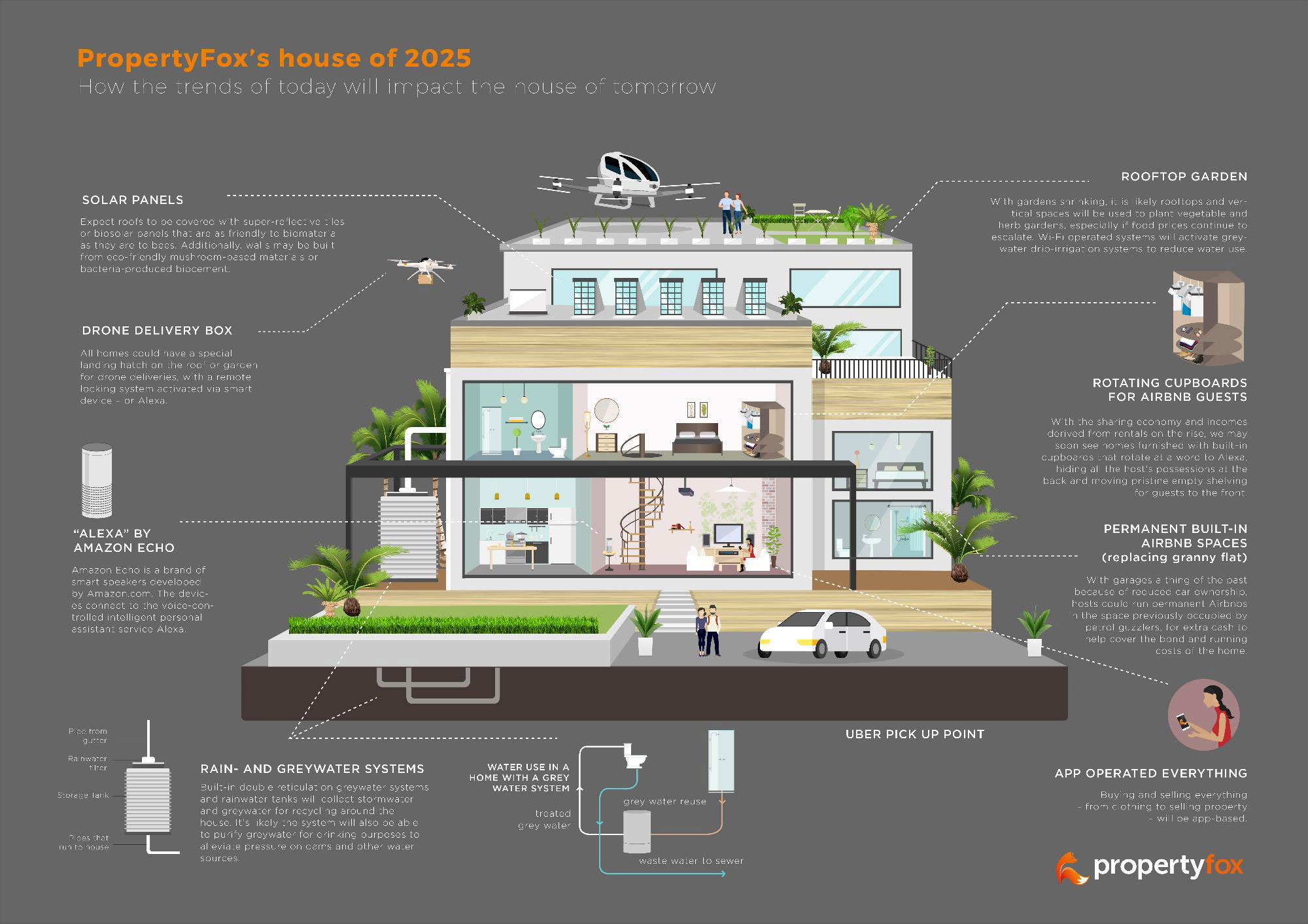
The construction industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the landscape of construction, impacting everything from project design and execution to workforce development and building performance. Understanding these trends is crucial for stakeholders – from architects and engineers to contractors and investors – to navigate the future of construction effectively.
Construction Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Overview
1. Sustainable Construction and Green Building:
- Emphasis on Environmental Responsibility: The construction industry is facing increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. Green building practices, encompassing energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of sustainable materials, are becoming the norm.
- Embracing Renewable Energy Sources: Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into building designs is gaining traction. This not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also lowers operational costs.
- Circular Economy Principles: The concept of a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled, is gaining momentum in construction. This approach minimizes waste and promotes resource conservation.
2. Digital Transformation and Advanced Technologies:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is no longer a novelty but a cornerstone of modern construction. Its ability to create detailed 3D models, simulate construction processes, and facilitate collaboration across disciplines has revolutionized project management and execution.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are finding applications in various aspects of construction, from site planning and scheduling to risk assessment and quality control. These technologies can optimize resource allocation, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making.
- Robotics and Automation: Robots are increasingly used for repetitive tasks such as bricklaying and welding, freeing up human workers for more skilled and complex roles. Automation also enhances safety and precision in construction operations.
3. Prefabrication and Modular Construction:
- Off-site Construction: Prefabrication, the process of manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment, is gaining popularity. This approach accelerates construction timelines, reduces on-site waste, and improves quality control.
- Modular Building Systems: Modular construction involves assembling pre-designed, pre-engineered building modules on-site. This method offers flexibility, cost savings, and faster construction times, particularly for large-scale projects.
4. Smart Cities and Connected Infrastructure:
- Smart Building Technologies: Smart buildings are equipped with sensors, data analytics, and automation systems to optimize energy consumption, enhance occupant comfort, and improve security.
- Integrated Infrastructure Systems: Smart cities require interconnected infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and communication systems, that can be monitored and managed efficiently.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data collected from sensors and building systems provides valuable insights for improving building performance, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing operational efficiency.
5. Emerging Materials and Construction Techniques:
- Lightweight Materials: The use of lightweight materials, such as composites and engineered wood, is gaining traction to reduce structural loads and enhance energy efficiency.
- 3D Printing in Construction: 3D printing technology is evolving rapidly, offering the potential to create complex structures and custom building components with greater speed and precision.
- Advanced Concrete Technologies: Innovations in concrete technology, including self-healing concrete and ultra-high-performance concrete, are enabling the construction of more durable and sustainable structures.
6. Focus on Workforce Development and Skills Gap:
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: The construction industry faces a growing skills gap, requiring innovative strategies to attract and retain skilled workers.
- Investing in Training and Education: Upskilling and reskilling programs are essential to equip workers with the knowledge and skills needed for the evolving construction landscape.
- Promoting Diversity and Inclusion: Creating a diverse and inclusive workforce is crucial to foster innovation and attract a wider pool of talent.
7. Increased Focus on Building Resilience and Adaptability:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Construction projects need to be designed and built to withstand the effects of climate change, including extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
- Disaster-Resistant Structures: Integrating resilience into building design and construction is paramount to minimize damage and ensure the safety of occupants during natural disasters.
- Adaptive Reuse and Retrofitting: Reusing existing buildings and retrofitting older structures to meet modern standards are crucial strategies for sustainable development and urban revitalization.
8. Collaboration and Partnerships:
- Cross-Industry Collaboration: Collaboration between construction professionals, architects, engineers, technology providers, and policymakers is essential to drive innovation and implement sustainable solutions.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Public-private partnerships can facilitate large-scale infrastructure projects and accelerate the adoption of new technologies and best practices.
- Open Innovation and Knowledge Sharing: Promoting open innovation and knowledge sharing within the construction industry can accelerate the development and adoption of new technologies and solutions.
Construction Trends 2025: Related Searches
1. Future of Construction Technology:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Construction: AI is transforming various aspects of construction, from project planning and scheduling to site safety and quality control. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data, identify potential risks, optimize resource allocation, and improve decision-making.
- Robotics and Automation in Construction: Robots are increasingly employed for repetitive and hazardous tasks, enhancing safety, precision, and efficiency. Examples include robotic bricklaying, welding, and concrete pouring.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Construction: VR and AR technologies are used for immersive site visualization, training simulations, and remote collaboration. They allow stakeholders to experience and interact with virtual models of construction projects.
2. Sustainable Construction Materials:
- Bio-based Materials: Bio-based materials derived from renewable sources, such as wood, bamboo, and hemp, offer sustainable alternatives to traditional construction materials.
- Recycled Materials: Incorporating recycled materials like recycled concrete, steel, and plastic into construction projects minimizes waste and reduces environmental impact.
- Geopolymer Concrete: Geopolymer concrete, a sustainable alternative to traditional Portland cement concrete, utilizes industrial byproducts and requires less energy to produce.
3. Smart Buildings and Smart Cities:
- Internet of Things (IoT) in Construction: IoT devices, such as sensors, actuators, and smart meters, are integrated into buildings to monitor energy consumption, optimize building performance, and enhance occupant comfort.
- Building Automation Systems: Automation systems control lighting, HVAC, and other building functions to optimize energy efficiency and improve operational efficiency.
- Smart City Infrastructure: Smart cities utilize integrated infrastructure systems, including transportation, energy, and communication networks, to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and livability.
4. Modular Construction and Prefabrication:
- Off-site Manufacturing: Prefabrication involves manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment, reducing on-site construction time, improving quality control, and minimizing waste.
- Modular Building Systems: Modular construction utilizes pre-designed and pre-engineered building modules that are assembled on-site, offering flexibility, cost savings, and faster construction times.
- Hybrid Construction Methods: Combining traditional construction techniques with prefabrication and modular elements can optimize project timelines, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency.
5. Construction Industry Trends in 2025:
- Construction Labor Shortage: The construction industry faces a significant labor shortage, driven by aging workforce demographics and a lack of skilled workers.
- Construction Industry Disruption: Technological advancements, changing regulations, and evolving consumer preferences are disrupting the construction industry, creating opportunities for innovation and adaptation.
- Construction Industry Growth: Despite challenges, the construction industry is expected to experience continued growth, driven by infrastructure development, urbanization, and increasing demand for housing.
6. Construction Project Management Trends:
- Lean Construction: Lean construction principles focus on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency throughout the construction process.
- Agile Construction: Agile construction methods emphasize iterative development, collaboration, and flexibility to adapt to changing project requirements.
- Project Delivery Methods: Various project delivery methods, such as design-build, construction management, and integrated project delivery, are employed to optimize project timelines, costs, and quality.
7. Construction Safety and Risk Management:
- Construction Safety Technology: Technologies such as wearable sensors, drones, and AI-powered safety systems are being used to enhance construction site safety.
- Risk Management Strategies: Comprehensive risk management strategies are crucial to identify and mitigate potential hazards throughout the construction lifecycle.
- Construction Safety Regulations: Stricter safety regulations and enforcement are essential to protect workers and minimize accidents on construction sites.
8. Construction Industry Sustainability:
- Sustainable Building Materials: Using sustainable materials, such as recycled content, renewable resources, and low-embodied energy materials, reduces the environmental impact of construction projects.
- Energy-Efficient Building Design: Designing buildings to optimize energy performance, including passive solar design, high-performance insulation, and efficient HVAC systems, reduces energy consumption and operating costs.
- Water Conservation in Construction: Implementing water conservation measures, such as rainwater harvesting, greywater reuse, and low-flow fixtures, minimizes water usage during construction and building operations.
Construction Trends 2025: FAQs
1. What are the key benefits of sustainable construction practices?
Sustainable construction practices offer numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Sustainable construction minimizes resource consumption, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved Building Performance: Energy-efficient buildings reduce operational costs and enhance occupant comfort.
- Enhanced Health and Well-being: Sustainable building materials and design principles promote indoor air quality, natural light, and healthy environments.
- Increased Asset Value: Green buildings often command higher property values and attract tenants seeking sustainable living spaces.
2. How is digital transformation changing the construction industry?
Digital transformation is revolutionizing the construction industry by:
- Enhancing Collaboration and Communication: Digital platforms facilitate seamless information sharing and collaboration among project stakeholders.
- Improving Project Planning and Scheduling: BIM and other digital tools enable detailed planning, simulation, and optimization of construction processes.
- Increasing Efficiency and Productivity: Automation, robotics, and AI-powered tools enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and accelerate construction timelines.
- Enhancing Safety and Risk Management: Digital technologies enable real-time monitoring of site conditions, identify potential hazards, and implement proactive safety measures.
3. What are the challenges associated with adopting prefabrication and modular construction?
While prefabrication and modular construction offer numerous advantages, they also present challenges:
- Initial Investment Costs: Setting up a factory and investing in specialized equipment for off-site manufacturing can involve significant upfront costs.
- Design Flexibility: Prefabricated components can sometimes limit design flexibility compared to traditional on-site construction.
- Transportation and Logistics: Transporting prefabricated components to the construction site requires careful planning and efficient logistics.
- Site Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between prefabricated components and existing site conditions is crucial for successful integration.
4. How can the construction industry address the skills gap and attract a new generation of workers?
Addressing the skills gap and attracting a new generation of workers requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Investing in Training and Education: Offering apprenticeships, vocational training programs, and industry-recognized certifications to develop a skilled workforce.
- Promoting STEM Education: Encouraging young people to pursue STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education to foster interest in construction-related fields.
- Highlighting Career Opportunities: Promoting the diverse and rewarding career opportunities available in the construction industry.
- Improving Work Conditions: Creating a positive and safe work environment to attract and retain talent.
5. What are the key considerations for designing resilient and adaptable buildings?
Designing resilient and adaptable buildings involves considering:
- Climate Change Impacts: Anticipating the effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events, sea level rise, and temperature fluctuations.
- Disaster Mitigation: Incorporating design features that minimize damage and ensure the safety of occupants during natural disasters.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Designing buildings that can be easily adapted to future needs and changes in occupancy or use.
- Sustainable Materials and Technologies: Utilizing durable and sustainable materials and technologies that contribute to building resilience.
Construction Trends 2025: Tips
1. Embrace Digital Technologies:
- Integrate BIM into project workflows to enhance planning, design, and construction management.
- Explore the use of AI and machine learning for data analysis, risk assessment, and decision-making.
- Adopt robotics and automation technologies for repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and safety.
2. Prioritize Sustainability:
- Incorporate sustainable materials, such as recycled content, bio-based materials, and low-embodied energy materials, into projects.
- Design energy-efficient buildings that minimize operational costs and environmental impact.
- Implement water conservation measures to reduce water usage during construction and building operations.
3. Focus on Workforce Development:
- Invest in training and education programs to upskill and reskill workers for the evolving construction landscape.
- Promote apprenticeships and vocational training to attract young talent to the industry.
- Create a positive and safe work environment to attract and retain skilled workers.
4. Embrace Collaboration and Partnerships:
- Foster collaboration among construction professionals, architects, engineers, technology providers, and policymakers to drive innovation.
- Explore public-private partnerships to facilitate large-scale infrastructure projects and accelerate the adoption of new technologies.
- Promote open innovation and knowledge sharing within the construction industry to accelerate the development and adoption of new solutions.
5. Stay Informed and Adaptable:
- Stay informed about emerging technologies, trends, and regulations impacting the construction industry.
- Continuously evaluate and adapt business models, project delivery methods, and construction practices to remain competitive.
- Embrace a culture of innovation and experimentation to explore new solutions and improve project outcomes.
Construction Trends 2025: Conclusion
The construction industry is on the cusp of a transformative era, driven by technological advancements, sustainability goals, and changing societal needs. By embracing the trends outlined in this article, stakeholders can navigate the evolving landscape, capitalize on new opportunities, and contribute to the development of a more sustainable, efficient, and resilient built environment. The future of construction is bright, and those who adapt and innovate will be well-positioned to shape the future of the industry.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Construction Trends in 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!