Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025
Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025
- 3.1 1. Personalized Nutrition and Dietary Needs
- 3.2 2. Plant-Based Diets and Alternative Proteins
- 3.3 3. Sustainable and Ethical Food Production
- 3.4 4. Food Tech and Automation
- 3.5 5. Food Waste Reduction and Circular Economy
- 3.6 6. Food Safety and Traceability
- 3.7 7. Urban Farming and Local Food Systems
- 3.8 8. Alternative Food Sources and Innovation
- 4 Related Searches
- 5 FAQs
- 6 Tips
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 Closure
Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025
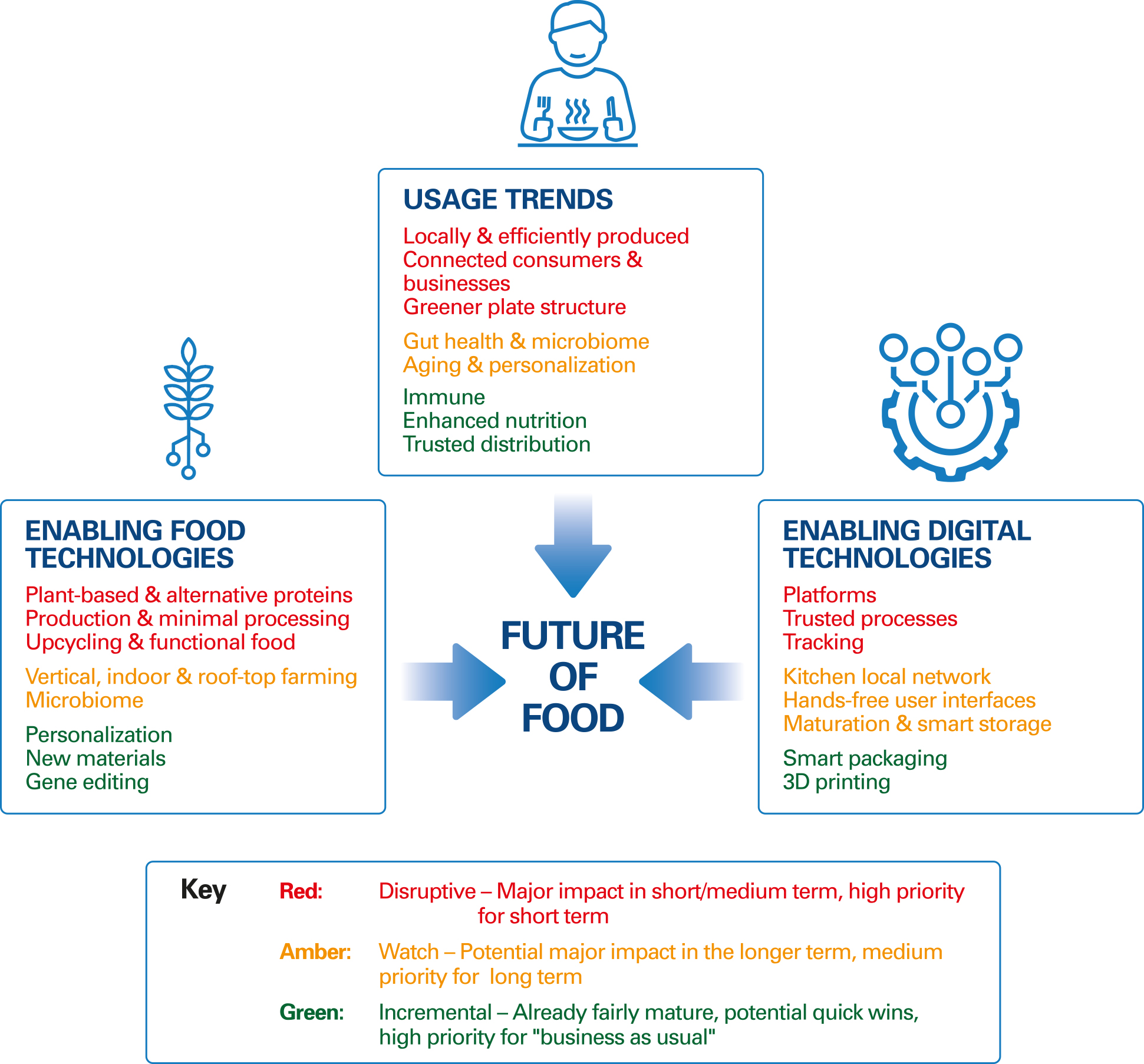
The food industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape. Driven by consumer demands, technological advancements, and environmental concerns, the industry is poised for significant transformation by 2025. This article delves into eight key trends shaping the future of food, providing insights into the forces driving change and the potential impact on consumers, businesses, and the planet.
1. Personalized Nutrition and Dietary Needs
The demand for personalized nutrition is on the rise, with consumers increasingly seeking diets tailored to their individual health goals, preferences, and dietary restrictions. This trend is fueled by growing awareness of the impact of food on health and the availability of technology that enables personalized dietary recommendations.
- Genomics and Precision Nutrition: Advances in genomics are enabling a deeper understanding of individual genetic predispositions to certain diseases and nutritional needs. This knowledge can be used to create personalized dietary plans that optimize health outcomes.
- Dietary Tracking Apps and Devices: Wearable devices and smartphone apps are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their ability to track dietary intake, physical activity, and other health metrics. This data allows for personalized recommendations and adjustments to dietary plans.
- Food Allergies and Intolerances: The prevalence of food allergies and intolerances is rising, driving the development of specialized food products and services catering to specific dietary needs. This includes allergen-free options, gluten-free products, and vegan or vegetarian alternatives.
Benefits:
- Improved health outcomes: Personalized nutrition can help individuals achieve specific health goals, manage chronic diseases, and improve overall well-being.
- Increased consumer satisfaction: Tailored dietary recommendations cater to individual preferences and needs, enhancing consumer satisfaction and engagement.
- Enhanced food innovation: The demand for personalized nutrition drives innovation in food product development and formulation, leading to a wider range of options for consumers.
2. Plant-Based Diets and Alternative Proteins
Plant-based diets are gaining popularity as consumers become more conscious of the environmental and health benefits of reducing meat consumption. This trend is driving the growth of alternative protein sources, such as plant-based meat alternatives, insect protein, and cultured meat.
- Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Companies are developing increasingly realistic and flavorful plant-based meat alternatives using ingredients like soy, pea protein, and mushrooms. These products are becoming increasingly popular as they offer a more sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional meat.
- Insect Protein: Insect protein is a highly efficient and sustainable source of protein that is gaining traction as a potential alternative to conventional animal protein.
- Cultured Meat: The development of cultured meat, grown from animal cells in a lab, is a promising solution for addressing ethical and environmental concerns related to traditional meat production.
Benefits:
- Reduced environmental impact: Plant-based diets and alternative proteins have a lower carbon footprint and require less land and water than traditional livestock farming.
- Improved animal welfare: The shift towards plant-based options reduces the demand for animal products, contributing to improved animal welfare.
- Enhanced health: Plant-based diets are often rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, promoting overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
3. Sustainable and Ethical Food Production
Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and ethical practices in food production. This includes concerns about environmental sustainability, animal welfare, and labor conditions.
- Organic and Sustainable Farming: Organic and sustainable farming practices are becoming more prevalent as consumers seek food produced with minimal environmental impact.
- Fair Trade and Ethical Sourcing: Consumers are increasingly interested in supporting fair trade and ethical sourcing practices that ensure fair wages and working conditions for farmers and workers.
- Reduced Food Waste: Food waste is a significant environmental and economic problem. The industry is actively working on reducing waste at all stages of the supply chain, from production to consumption.
Benefits:
- Environmental protection: Sustainable and ethical food production practices help protect the environment, conserve natural resources, and reduce pollution.
- Improved social equity: Fair trade and ethical sourcing initiatives promote fair wages, safe working conditions, and social justice for farmers and workers.
- Economic sustainability: Reducing food waste and promoting sustainable practices contribute to economic sustainability by reducing costs and improving resource efficiency.
4. Food Tech and Automation
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in the food industry, from farm-to-fork. This includes advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics.
- Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture techniques, such as sensors, drones, and data analytics, optimize crop yields, reduce water and fertilizer use, and enhance farm efficiency.
- Food Processing Automation: Automation is being implemented in food processing plants to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and ensure consistent product quality.
- Food Delivery and Logistics: Technology is transforming food delivery and logistics, with platforms like online ordering, delivery apps, and automated warehousing streamlining the process and enhancing convenience.
Benefits:
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Automation and technology improve efficiency in food production, processing, and distribution, leading to lower costs and increased productivity.
- Improved food safety and quality: Technology enables better monitoring and control of food safety and quality throughout the supply chain.
- Enhanced consumer experience: Technology enhances convenience and accessibility for consumers, providing a wider range of food options and delivery services.
5. Food Waste Reduction and Circular Economy
Food waste is a major global problem, with significant environmental, economic, and social implications. The food industry is actively seeking solutions to reduce food waste at all stages of the supply chain.
- Improved Packaging: Innovative packaging solutions, such as biodegradable and compostable materials, are being developed to extend shelf life and reduce food waste.
- Food Waste Recovery and Upcycling: Technologies are being developed to recover nutrients and energy from food waste, converting it into valuable resources.
- Consumer Education and Awareness: Raising consumer awareness about food waste and providing practical tips for reducing waste at home is crucial for driving change.
Benefits:
- Reduced environmental impact: Reducing food waste helps conserve natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize landfill waste.
- Economic benefits: Reducing food waste lowers costs for businesses and consumers, improving economic efficiency.
- Social impact: Addressing food waste helps ensure food security and reduce food insecurity, particularly in vulnerable communities.
6. Food Safety and Traceability
Food safety is a paramount concern for consumers and businesses alike. Advances in technology are enabling enhanced traceability and transparency in the food supply chain.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can be used to track food products from origin to consumer, providing a secure and transparent record of their journey.
- Sensors and Monitoring Systems: Sensors and monitoring systems can be used to track key parameters, such as temperature and humidity, ensuring optimal storage conditions and food safety.
- Rapid Detection Technologies: Advanced technologies are being developed for rapid detection of foodborne pathogens and contaminants, improving food safety and preventing outbreaks.
Benefits:
- Enhanced food safety: Traceability and transparency improve food safety by enabling quick identification and response to potential contamination or safety issues.
- Increased consumer confidence: Consumers are more likely to trust food products that are traceable and transparent, leading to increased consumer confidence and loyalty.
- Improved supply chain management: Traceability helps businesses manage their supply chains more effectively, identify potential bottlenecks, and improve efficiency.
7. Urban Farming and Local Food Systems
Urban farming and local food systems are gaining popularity as consumers seek fresh, locally sourced food and support their communities.
- Vertical Farming: Vertical farming techniques allow for growing crops in stacked layers, maximizing space and reducing the need for land.
- Community Gardens: Community gardens provide opportunities for urban residents to grow their own food, promote social interaction, and create a sense of community.
- Local Food Markets: Local food markets connect consumers with local farmers and producers, providing access to fresh, seasonal produce and supporting local economies.
Benefits:
- Increased food security: Local food systems enhance food security by reducing reliance on long-distance transportation and global supply chains.
- Reduced environmental impact: Local food production reduces transportation distances, lowering carbon emissions and supporting sustainable agriculture.
- Community building: Urban farming and local food systems foster a sense of community, promoting social interaction and shared responsibility for food production.
8. Alternative Food Sources and Innovation
The food industry is constantly innovating and exploring new food sources to address growing population needs and environmental concerns.
- Microalgae and Seaweed: Microalgae and seaweed are nutrient-rich and sustainable sources of food, protein, and biofuels.
- Lab-Grown Meat: Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat, is a promising alternative to traditional meat production, offering a more sustainable and ethical option.
- Food Printing: 3D food printing technology allows for the creation of customized and personalized food products with unique shapes, textures, and flavors.
Benefits:
- Sustainable food production: Alternative food sources offer a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to food production.
- Novel food experiences: Innovation in food technology and sources leads to new and exciting food experiences, expanding culinary horizons.
- Addressing food security: Exploring new food sources helps address the growing demand for food as the global population increases.
Related Searches
The trends outlined above are interconnected and contribute to a broader shift in the food industry. Exploring these related searches provides further insights into the future of food:
- Food Trends 2025: This search explores broader trends in consumer preferences, dietary choices, and emerging food concepts.
- Future of Food: This search examines long-term projections for the food industry, including technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and societal changes.
- Food Industry Innovations: This search focuses on specific innovations and technologies driving change in the food industry, from production to consumption.
- Sustainable Food Systems: This search delves into the broader concept of sustainable food systems, encompassing production, distribution, consumption, and waste management.
- Food Security and Nutrition: This search explores the challenges and solutions related to ensuring food security and improving nutritional outcomes for all.
- Impact of Climate Change on Food: This search examines the impact of climate change on food production, distribution, and consumption, highlighting the need for adaptation and mitigation strategies.
- Food Waste Solutions: This search focuses on specific solutions and initiatives aimed at reducing food waste at all stages of the supply chain.
- Food Safety and Regulation: This search explores the evolving regulatory landscape for food safety and the role of technology in ensuring food safety and quality.
FAQs
1. What are the biggest challenges facing the food industry in 2025?
The food industry faces numerous challenges, including climate change, food security, resource scarcity, and consumer demands for sustainability and ethical practices. Balancing economic viability with environmental and social responsibility is a key challenge.
2. How will technology impact the food industry in the future?
Technology is expected to play a transformative role in the food industry, driving innovation in areas like precision agriculture, automation, food safety, and traceability. These advancements will enhance efficiency, productivity, and consumer experiences.
3. What are the key factors driving the shift towards plant-based diets?
Consumer awareness of the environmental impact of meat production, health concerns related to red meat consumption, and the growing availability of realistic and flavorful plant-based alternatives are driving the shift towards plant-based diets.
4. How can the food industry reduce food waste?
Reducing food waste requires a multi-pronged approach, including improved packaging, food waste recovery and upcycling, consumer education, and collaboration across the supply chain.
5. What are the benefits of urban farming and local food systems?
Urban farming and local food systems promote food security, reduce environmental impact, foster community building, and support local economies.
6. How will the food industry adapt to changing consumer preferences?
The food industry must adapt to changing consumer preferences by offering personalized nutrition, plant-based options, sustainable products, and transparent and ethical sourcing practices.
7. What are the ethical considerations surrounding alternative food sources?
Ethical considerations surrounding alternative food sources include the potential impact on biodiversity, animal welfare, and consumer acceptance. Transparency and responsible innovation are crucial for addressing these concerns.
8. How can consumers contribute to a more sustainable food system?
Consumers can contribute to a more sustainable food system by choosing sustainable and ethical products, reducing food waste, supporting local food systems, and advocating for policies that promote sustainability.
Tips
- Be informed about food trends and innovations: Stay informed about emerging trends and innovations in the food industry to make informed choices as a consumer and a citizen.
- Support sustainable and ethical food production: Choose products from companies committed to sustainable and ethical practices, such as organic farming, fair trade, and animal welfare.
- Reduce food waste: Implement strategies at home to reduce food waste, such as proper storage, meal planning, and composting.
- Explore plant-based options: Experiment with plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy products to reduce your environmental footprint and support a more sustainable food system.
- Support local food systems: Purchase fresh produce and products from local farmers and producers to support your community and promote sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion
The food industry is on the cusp of significant transformation, driven by consumer demands, technological advancements, and environmental concerns. The trends outlined in this article highlight the key forces shaping the future of food, emphasizing the importance of sustainability, innovation, and consumer engagement. By embracing these trends and working collaboratively, the food industry can create a more sustainable, equitable, and nutritious food system for all.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future Plate: Trends in the Food Industry 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!