The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025
The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025
- 3.1 Understanding Bond Energy Trends
- 3.2 The Significance of Bond Energy Trends
- 3.3 Bond Energy Trends in 2025 and Beyond
- 3.4 Related Searches
- 3.5 FAQs on Bond Energy Trends
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding Bond Energy Trends
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025

The realm of chemistry is built upon the fundamental concept of chemical bonds, the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and materials. Understanding the strengths of these bonds, quantified by bond energy, is crucial for predicting and controlling chemical reactions, designing novel materials, and even understanding the workings of life itself.
As we move into the future, the field of chemistry is poised for significant advancements, driven by innovative technologies and a growing need for sustainable solutions. Bond energy trends are at the heart of this progress, influencing the development of new catalysts, energy storage systems, and advanced materials.
Understanding Bond Energy Trends
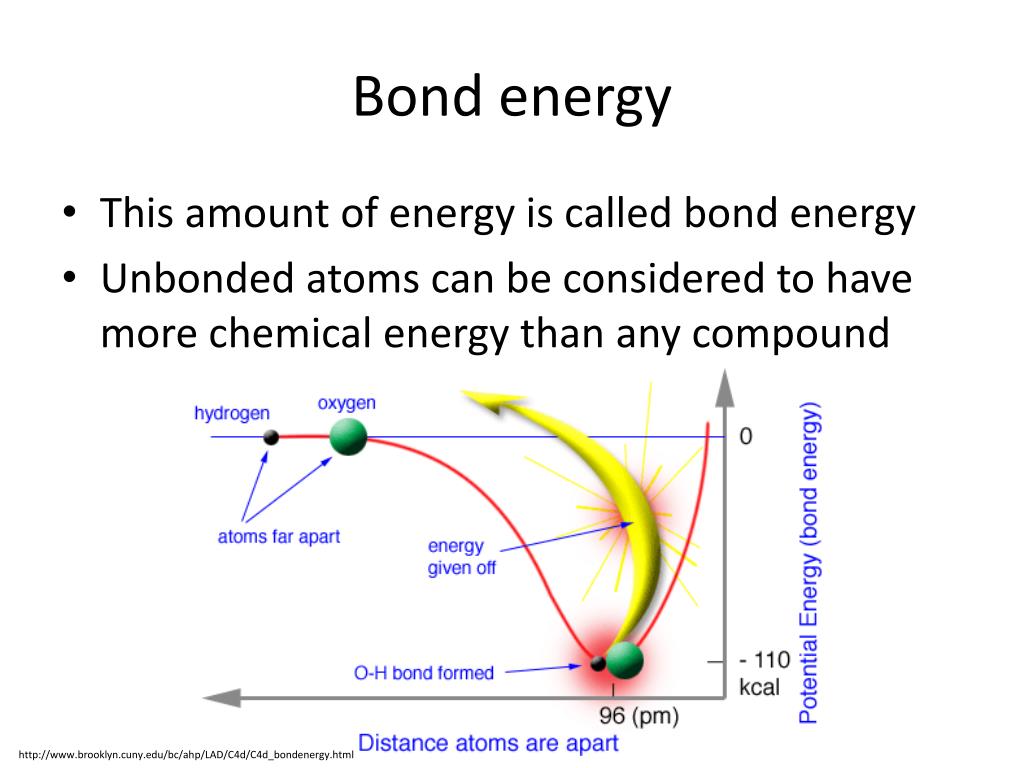
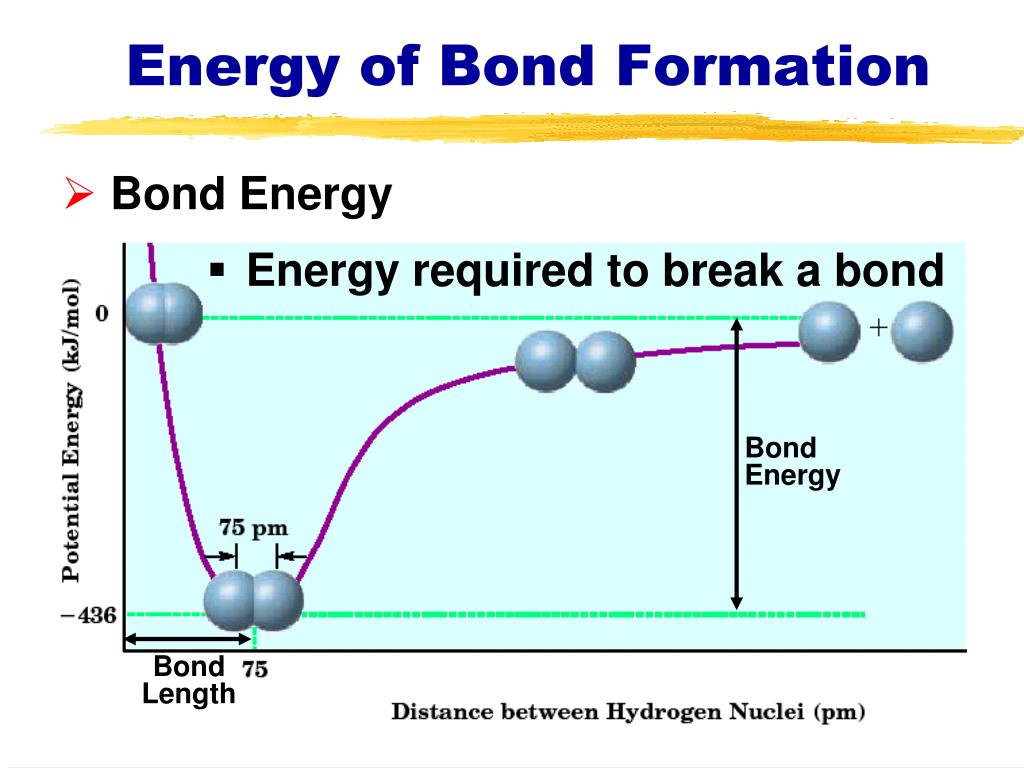
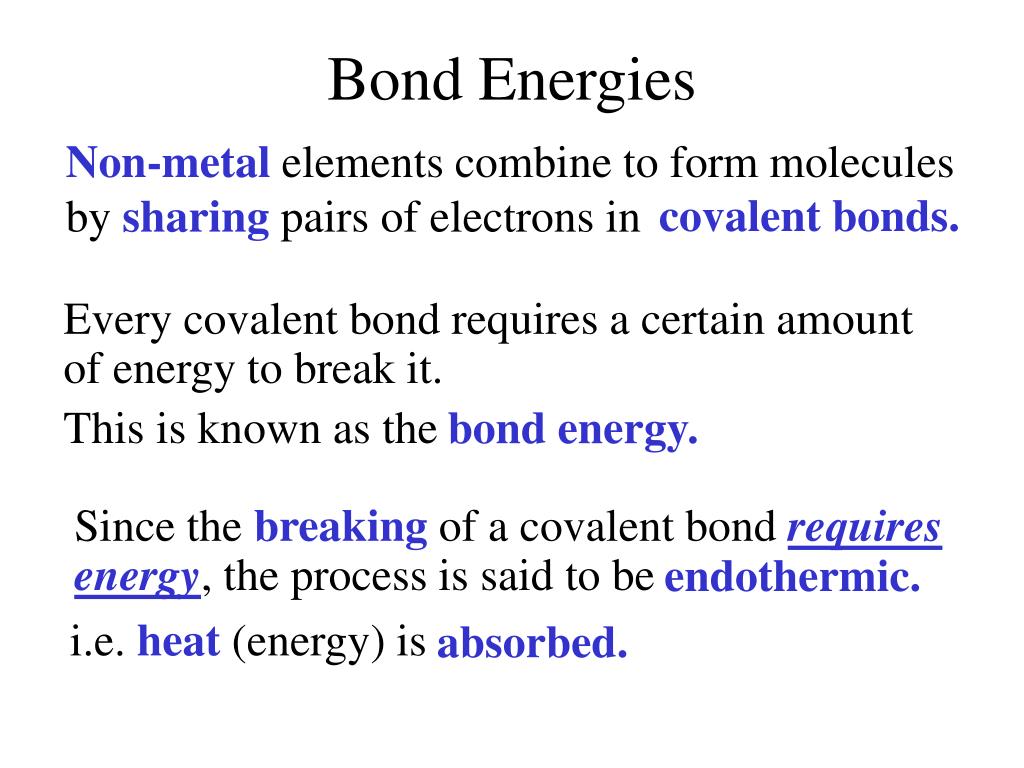
Bond energy refers to the amount of energy required to break a specific bond between two atoms in a molecule. It is a measure of the strength of the bond, with higher bond energies indicating stronger bonds. This energy is typically expressed in units of kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol).
Bond energy trends are observed patterns in the strengths of chemical bonds based on factors like:
- Nature of the atoms involved: The type of atoms forming the bond significantly impacts its strength. For example, a carbon-carbon bond is generally stronger than a carbon-hydrogen bond.
- Bond multiplicity: Double and triple bonds are generally stronger than single bonds due to increased electron sharing.
- Bond length: Shorter bonds tend to be stronger due to increased electron density between the atoms.
- Electronegativity differences: Bonds between atoms with similar electronegativities (ability to attract electrons) are generally stronger than those with large differences.
The Significance of Bond Energy Trends
The study of bond energy trends is vital for several reasons:
- Predicting reaction outcomes: Knowing the relative strengths of bonds involved in a reaction helps predict whether the reaction will be exothermic (releases heat) or endothermic (requires heat).
- Designing new materials: Understanding bond energies allows chemists to design materials with specific properties, such as high melting points, strength, or conductivity.
- Developing efficient catalysts: Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy of reactions, often by weakening specific bonds. Understanding bond energy trends is crucial for designing effective catalysts.
- Understanding biological processes: Many biological processes rely on the formation and breaking of chemical bonds. Understanding bond energies helps unravel the complexities of these processes.
Bond Energy Trends in 2025 and Beyond
Looking towards 2025 and beyond, several key bond energy trends are shaping the future of chemistry:
- Computational chemistry: Advancements in computational power and modeling techniques allow for accurate prediction of bond energies, even for complex molecules. This enables researchers to explore new chemical reactions and design novel materials without extensive laboratory experimentation.
- Nanomaterials and nanotechnology: The development of nanomaterials with unique properties relies heavily on understanding the interplay of bond strengths at the nanoscale. This includes designing materials with enhanced strength, conductivity, and catalytic activity.
- Sustainable energy: The transition to a sustainable energy future necessitates the development of efficient energy storage and conversion technologies. Understanding bond energy trends is crucial for designing advanced batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells.
- Biochemistry and drug development: Understanding bond energies within biological molecules is vital for developing new pharmaceuticals and therapies. This involves designing drugs that target specific molecules by interacting with their bonds, ultimately influencing their function.
Related Searches
Here are eight related searches that provide a deeper understanding of the intricacies surrounding bond energy trends:
1. Bond Energy Calculation: This search focuses on the various methods and techniques used to calculate bond energies, both theoretically and experimentally. It explores the use of quantum chemistry methods, thermochemical data analysis, and spectroscopic techniques.
2. Bond Energy Table: This search leads to comprehensive tables that list bond energies for a wide range of chemical bonds. These tables are invaluable resources for chemists, providing quick access to bond energy values for various molecules and functional groups.
3. Bond Energy and Reaction Enthalpy: This search delves into the relationship between bond energies and the enthalpy change of chemical reactions. It explores how bond energies can be used to estimate reaction enthalpy and understand the heat released or absorbed during a reaction.
4. Bond Energy and Reaction Mechanism: This search examines the role of bond energies in understanding the mechanism of chemical reactions. It explores how the breaking and forming of bonds can be used to explain the steps involved in a reaction and the formation of intermediates.
5. Bond Energy and Molecular Stability: This search explores the connection between bond energies and the stability of molecules. It examines how strong bonds contribute to the overall stability of a molecule and how weak bonds can lead to instability and reactivity.
6. Bond Energy and Spectroscopy: This search explores the use of spectroscopic techniques, such as infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy, to study bond energies. These techniques provide information about the vibrational frequencies of molecules, which can be used to determine bond strengths.
7. Bond Energy and Catalysis: This search focuses on the role of bond energies in catalysis. It explores how catalysts can influence the breaking and forming of bonds, thereby accelerating chemical reactions and enhancing their efficiency.
8. Bond Energy and Materials Science: This search delves into the application of bond energy principles in materials science. It examines how bond energies influence the properties of materials, such as strength, hardness, melting point, and conductivity, and how these properties can be tailored by controlling bond strengths.
FAQs on Bond Energy Trends
1. How are bond energies measured?
Bond energies can be determined experimentally using various techniques, including:
- Calorimetry: This method measures the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction, which can be used to calculate the bond energies involved.
- Spectroscopy: Techniques like infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy provide information about the vibrational frequencies of molecules, which can be related to bond strengths.
- Quantum chemistry calculations: Advancements in computational chemistry allow for the theoretical calculation of bond energies using sophisticated software programs.
2. How do bond energies vary with the type of bond?
Bond energies vary significantly depending on the type of bond. Some general trends include:
- Covalent bonds: These bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. The strength of a covalent bond depends on factors like the type of atoms involved, the number of shared electrons, and the bond length.
- Ionic bonds: These bonds are formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. The strength of an ionic bond depends on the charges of the ions and the distance between them.
- Metallic bonds: These bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons between a lattice of metal atoms. The strength of a metallic bond depends on the number of valence electrons and the size of the metal atoms.
3. How do bond energies affect chemical reactions?
Bond energies play a crucial role in determining the feasibility and rate of chemical reactions.
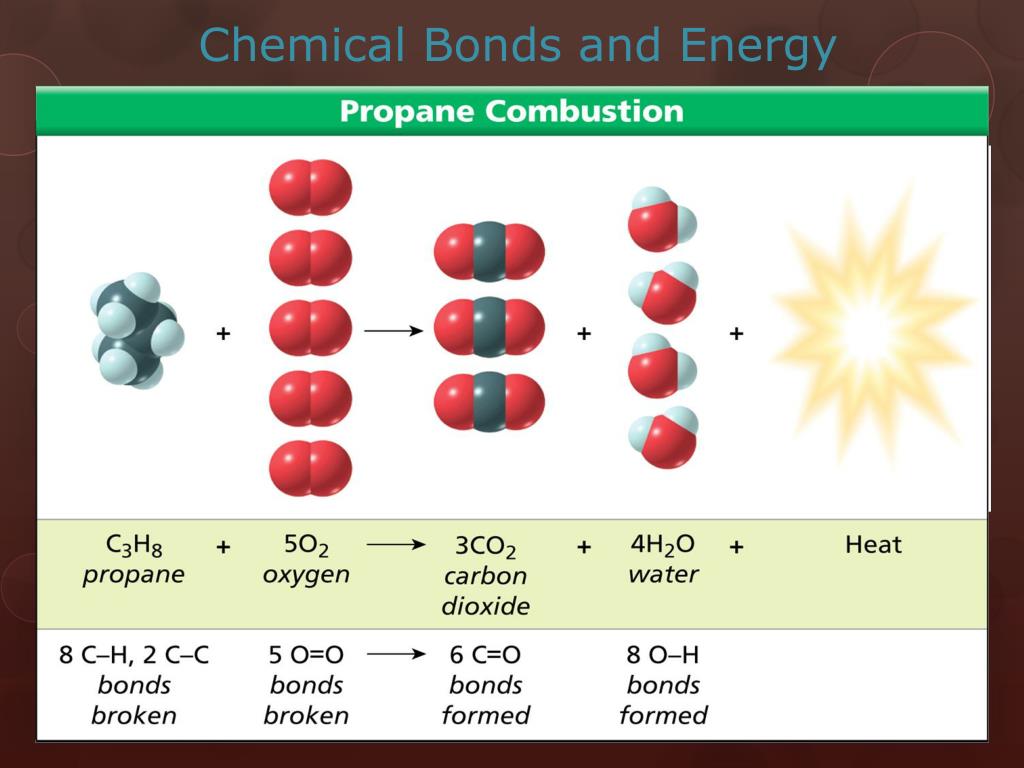
- Reaction enthalpy: The change in enthalpy (heat) during a reaction can be estimated by comparing the bond energies of the reactants and products. If the total bond energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants, the reaction is exothermic and releases heat. Conversely, if the bond energy of the products is higher, the reaction is endothermic and requires heat.
- Activation energy: The activation energy is the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur. Breaking existing bonds in reactants requires energy, while forming new bonds in products releases energy. The difference between these energies determines the activation energy.
4. What are the future implications of bond energy trends?
The understanding of bond energy trends is crucial for driving advancements in various fields, including:
- Materials science: Designing materials with specific properties like strength, conductivity, and thermal stability relies heavily on understanding bond energies.
- Catalysis: Developing efficient catalysts for various industrial processes requires a deep understanding of bond energies and their influence on reaction pathways.
- Drug development: Designing new drugs that target specific molecules and biological pathways often involves manipulating bond strengths to achieve desired therapeutic effects.
- Energy storage: Developing efficient energy storage technologies, such as batteries and fuel cells, necessitates understanding bond energies and their role in storing and releasing energy.
Tips for Understanding Bond Energy Trends
- Focus on the basics: Begin by understanding the fundamental concepts of chemical bonds, including the types of bonds, bond length, and bond multiplicity.
- Study periodic trends: Familiarize yourself with periodic trends, such as electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius, as these influence bond strengths.
- Use bond energy tables: Refer to bond energy tables to compare the strengths of different bonds and identify patterns.
- Apply knowledge to reactions: Use your understanding of bond energies to predict the outcome of chemical reactions and explain their mechanisms.
- Explore computational chemistry: Learn about computational chemistry tools and techniques that allow for the prediction of bond energies and the design of new molecules.
Conclusion
Bond energy trends are fundamental to our understanding of chemistry, impacting everything from the design of new materials to the development of life-saving drugs. As our knowledge of bond energies continues to evolve, so too will our ability to harness the power of chemistry to create a brighter future. By understanding the intricate interplay of forces that hold atoms together, we can unlock new possibilities and address some of the most pressing challenges facing our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolving Landscape of Chemical Bonds: A Look at Bond Energy Trends in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!