The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025
The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
- 3.2 2. The Evolution of Cloud Security
- 3.3 3. The Rise of Edge Computing
- 3.4 4. The Growth of Serverless Computing
- 3.5 5. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 3.6 6. The Importance of Cloud-Native Development
- 3.7 7. The Rise of Quantum Computing
- 3.8 8. The Importance of Sustainability in Cloud Computing
- 3.9 Related Searches
- 3.10 FAQs about Trends of Cloud Computing in 2025
- 3.11 Tips for Businesses Embracing Trends of Cloud Computing in 2025
- 3.12 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025
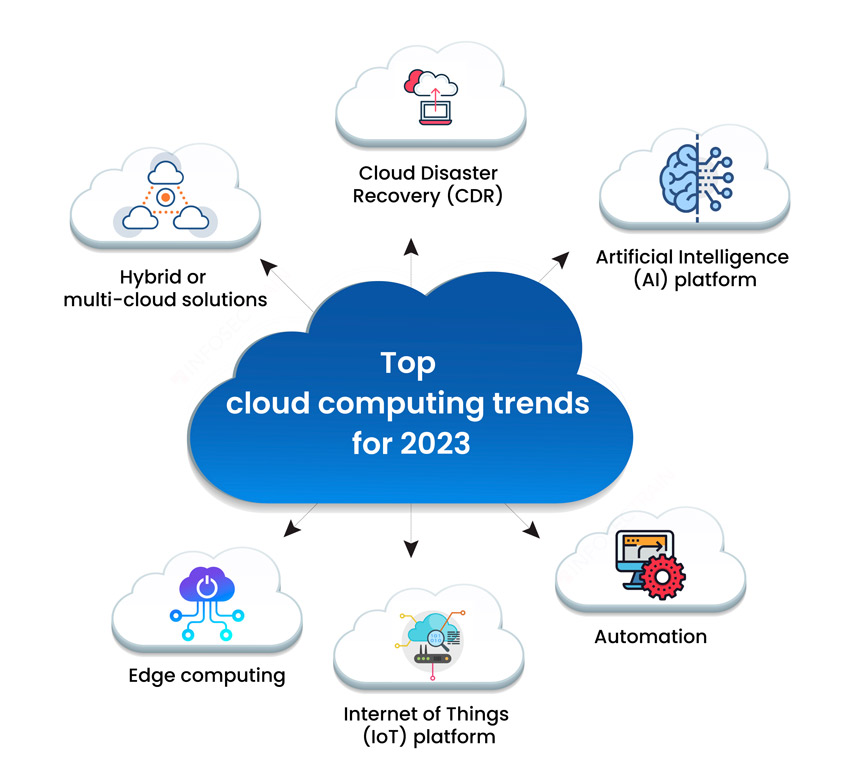
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective infrastructure for everything from data storage to application development. As we move closer to 2025, the cloud landscape is undergoing a dynamic transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving user demands, and a rapidly changing global environment. This article delves into the key trends of cloud computing in 2025, exploring their implications for businesses and the future of the technology itself.
1. The Rise of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
The days of relying solely on a single cloud provider are fading. Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to achieve greater flexibility, resilience, and cost optimization.
Multi-cloud refers to utilizing multiple cloud providers simultaneously, leveraging the strengths of each platform to meet specific business needs. This approach offers enhanced flexibility, avoiding vendor lock-in and allowing organizations to choose the best solution for each workload.
Hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services. This approach provides a balance between the control and security of on-premises solutions and the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies:
- Increased Flexibility: Businesses can choose the best cloud provider for each workload, optimizing performance and costs.
- Enhanced Resilience: Diversifying cloud providers minimizes the impact of outages or service disruptions.
- Cost Optimization: Organizations can leverage competitive pricing from different cloud providers to minimize expenditure.
- Improved Security: Implementing multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies can enhance security by distributing data and applications across different platforms.
Challenges of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies:
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud environments can be challenging, requiring specialized skills and tools.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring consistent security across multiple cloud platforms requires robust security protocols and vigilant monitoring.
- Data Management: Managing data across multiple cloud platforms can be complex, requiring efficient data governance and management strategies.
2. The Evolution of Cloud Security
As cloud adoption continues to grow, so too does the need for robust security measures. The cloud landscape is constantly evolving, presenting new challenges and opportunities for attackers. This has led to a focus on proactive security measures, including:
- Zero Trust Security: This approach assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict authentication and authorization for every access attempt.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud environments for misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and policy violations, enabling organizations to identify and remediate security risks proactively.
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs): CWPPs provide comprehensive security solutions for cloud workloads, encompassing runtime protection, threat detection, and response capabilities.
- Cloud-Native Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Cloud-native SIEM solutions offer centralized logging, analysis, and threat detection capabilities, enabling organizations to identify and respond to security incidents in real time.
Benefits of Enhanced Cloud Security:
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Proactive security measures minimize the likelihood of successful attacks, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Improved Compliance: Robust security measures help organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as HIPAA and GDPR.
- Enhanced Business Continuity: Security breaches can disrupt business operations. Strong cloud security measures ensure business continuity by mitigating the impact of attacks.
Challenges of Cloud Security:
- Complexity: Implementing comprehensive cloud security measures requires specialized expertise and ongoing maintenance.
- Evolving Threats: The cloud security landscape is constantly evolving, requiring organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining robust cloud security measures can be expensive, requiring significant investment in technology and personnel.
3. The Rise of Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This approach is particularly beneficial for applications requiring low latency, such as real-time streaming, gaming, and IoT devices.
Benefits of Edge Computing:
- Reduced Latency: Processing data closer to the source minimizes network delays, improving application performance and user experience.
- Improved Responsiveness: Real-time data processing enables faster decision-making and more responsive applications.
- Increased Bandwidth Efficiency: Processing data locally reduces reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure, optimizing bandwidth usage.
- Enhanced Data Security: Data processed at the edge is less vulnerable to security breaches, as it does not need to travel across the network to a centralized data center.
Challenges of Edge Computing:
- Complexity: Deploying and managing edge computing infrastructure can be complex, requiring specialized expertise and tools.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring security at the edge is crucial, as edge devices are often more vulnerable to attacks.
- Cost: Implementing edge computing infrastructure can be expensive, requiring investment in hardware, software, and management.
4. The Growth of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows developers to run code without managing servers, simplifying application development and deployment. This approach eliminates the need for infrastructure provisioning and maintenance, enabling developers to focus on building applications.
Benefits of Serverless Computing:
- Simplified Development: Developers can focus on building applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
- Improved Scalability: Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Cost Optimization: Pay-as-you-go pricing models eliminate the need for idle server capacity, reducing costs.
- Enhanced Agility: Serverless computing enables rapid deployment and iteration, accelerating development cycles and time to market.
Challenges of Serverless Computing:
- Vendor Lock-in: Relying heavily on a single serverless provider can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and options.
- Cold Starts: Serverless functions can experience cold starts, where initial execution takes longer due to the need to provision resources.
- Debugging and Monitoring: Debugging and monitoring serverless applications can be challenging, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
5. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming the cloud computing landscape, enabling intelligent automation, data analysis, and predictive insights.
Cloud-based AI and ML solutions offer:
- Enhanced Data Analysis: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns, trends, and insights, enabling better decision-making.
- Automated Processes: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities.
- Predictive Insights: AI and ML models can predict future outcomes based on historical data, enabling proactive decision-making and risk mitigation.
- Personalized Experiences: AI and ML can personalize user experiences, tailoring content and recommendations based on individual preferences.
Benefits of AI and ML in Cloud Computing:
- Improved Efficiency: AI and ML can automate tasks, optimize processes, and enhance productivity.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI and ML can provide insights and predictions, enabling better-informed decisions.
- Increased Innovation: AI and ML can unlock new possibilities for innovation, creating new products and services.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses leveraging AI and ML can gain a competitive edge by offering innovative solutions and better customer experiences.
Challenges of AI and ML in Cloud Computing:
- Data Quality: AI and ML models rely on high-quality data for accurate results. Ensuring data quality and consistency is crucial.
- Model Bias: AI and ML models can exhibit bias if trained on biased data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Ethical Considerations: Implementing AI and ML solutions raises ethical considerations, such as data privacy, transparency, and accountability.
6. The Importance of Cloud-Native Development
Cloud-native development refers to building and deploying applications specifically for cloud environments, leveraging cloud-native technologies and principles. This approach enables organizations to build scalable, resilient, and cost-effective applications.
Key Principles of Cloud-Native Development:
- Microservices Architecture: Breaking down applications into small, independent services, enabling modularity, scalability, and independent deployment.
- Containers and Orchestration: Using containers to package applications and their dependencies, simplifying deployment and management.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Automating the build, test, and deployment process, enabling faster delivery and improved quality.
- DevOps Practices: Fostering collaboration between development and operations teams, streamlining workflows and improving communication.
Benefits of Cloud-Native Development:
- Improved Scalability: Cloud-native applications can scale up or down automatically based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Enhanced Resilience: Microservices architecture and containerization enable fault tolerance and disaster recovery, minimizing downtime.
- Faster Time to Market: CI/CD pipelines accelerate development cycles, enabling faster delivery of new features and updates.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud-native applications are designed for efficient resource utilization, reducing infrastructure costs.
Challenges of Cloud-Native Development:
- Complexity: Cloud-native development requires specialized skills and tools, adding complexity to the development process.
- Security Concerns: Securing cloud-native applications requires a holistic approach, encompassing infrastructure, applications, and data.
- Vendor Lock-in: Relying heavily on cloud-native technologies and platforms can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and options.
7. The Rise of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems that are intractable for traditional computers. While still in its early stages, quantum computing holds immense potential for transforming various industries, including healthcare, finance, and materials science.
Potential Applications of Quantum Computing in Cloud Computing:
- Drug Discovery and Development: Quantum computers can accelerate the process of drug discovery by simulating complex molecular interactions.
- Financial Modeling: Quantum algorithms can optimize financial portfolios and improve risk management strategies.
- Materials Science: Quantum computing can be used to design new materials with improved properties.
- Cryptography: Quantum computing poses a threat to existing encryption algorithms, driving the need for quantum-resistant cryptography.
Benefits of Quantum Computing in Cloud Computing:
- Enhanced Computational Power: Quantum computers offer exponential speedups for certain types of problems, enabling breakthroughs in various fields.
- New Possibilities for Innovation: Quantum computing unlocks new possibilities for innovation, driving advancements in medicine, materials science, and other fields.
- Improved Efficiency: Quantum algorithms can optimize complex processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses leveraging quantum computing can gain a competitive advantage by developing innovative solutions and services.
Challenges of Quantum Computing in Cloud Computing:
- Technological Immaturity: Quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, with significant technical challenges to overcome.
- Cost and Complexity: Quantum computers are expensive to build and operate, requiring specialized expertise and infrastructure.
- Limited Availability: Access to quantum computing resources is currently limited, hindering widespread adoption.
8. The Importance of Sustainability in Cloud Computing
As cloud computing grows in scale and complexity, the need for sustainable practices becomes increasingly important. Cloud providers and businesses are taking steps to minimize their environmental impact, including:
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizing data centers for energy efficiency, using renewable energy sources, and implementing green data center designs.
- Carbon Offsetting: Investing in carbon offset projects to compensate for emissions associated with cloud operations.
- Sustainable Procurement: Sourcing hardware and software from suppliers committed to sustainable practices.
- Cloud Optimization: Implementing cloud optimization strategies to minimize resource usage and reduce energy consumption.
Benefits of Sustainable Cloud Computing:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimizing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices to mitigate climate change.
- Cost Savings: Energy efficiency measures can reduce operating costs and improve profitability.
- Improved Brand Image: Demonstrating commitment to sustainability can enhance brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious customers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting growing regulatory requirements for environmental sustainability.
Challenges of Sustainable Cloud Computing:
- Cost: Implementing sustainable practices can require significant upfront investments.
- Technological Limitations: Current technologies may not always provide the most efficient and sustainable solutions.
- Limited Data Availability: Accurate data on the environmental impact of cloud services is often limited, making it challenging to measure progress.
Related Searches
Trends of Cloud Computing 2025
- Future of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Trends 2024
- Cloud Computing Market Size
- Cloud Computing Services
- Cloud Computing Benefits
- Cloud Computing Security
- Cloud Computing Architecture
- Cloud Computing Applications
FAQs about Trends of Cloud Computing in 2025
Q: What are the key benefits of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies?
A: Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies offer increased flexibility, enhanced resilience, cost optimization, and improved security. By diversifying cloud providers and combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, businesses can achieve greater agility and control over their IT environments.
Q: How is cloud security evolving in 2025?
A: Cloud security is evolving to address the growing complexity and sophistication of cyber threats. Key trends include zero trust security, cloud security posture management (CSPM), cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), and cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM). These solutions provide proactive security measures, continuous monitoring, and automated threat detection and response capabilities.
Q: What are the potential applications of quantum computing in cloud computing?
A: Quantum computing holds immense potential for transforming various industries. In cloud computing, it could accelerate drug discovery, optimize financial models, design new materials, and enhance cryptography. However, quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, and its widespread adoption is not expected for several years.
Q: What steps can businesses take to ensure sustainable cloud computing practices?
A: Businesses can promote sustainable cloud computing by optimizing data centers for energy efficiency, using renewable energy sources, investing in carbon offset projects, sourcing hardware and software from sustainable suppliers, and implementing cloud optimization strategies to minimize resource usage.
Tips for Businesses Embracing Trends of Cloud Computing in 2025
- Adopt a Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Cloud Strategy: Leverage the strengths of different cloud providers to optimize performance, costs, and resilience.
- Invest in Cloud Security: Implement comprehensive security measures, including zero trust security, CSPM, CWPPs, and cloud-native SIEM, to protect sensitive data and ensure business continuity.
- Explore Edge Computing: Consider edge computing for applications requiring low latency, such as real-time streaming, gaming, and IoT devices.
- Embrace Serverless Computing: Simplify application development and deployment by leveraging serverless platforms.
- Integrate AI and ML: Utilize AI and ML solutions to enhance data analysis, automate processes, and gain predictive insights.
- Adopt Cloud-Native Development: Build and deploy applications specifically for cloud environments, leveraging cloud-native technologies and principles.
- Stay Informed about Quantum Computing: Monitor the development of quantum computing and explore potential applications for your business.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Implement sustainable cloud computing practices to minimize environmental impact and enhance brand reputation.
Conclusion
The cloud computing landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing user demands, and a rapidly changing global environment. As we move closer to 2025, businesses need to embrace the key trends of cloud computing to remain competitive and achieve their strategic goals. By adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, prioritizing cloud security, exploring edge computing, embracing serverless computing, integrating AI and ML, adopting cloud-native development, staying informed about quantum computing, and prioritizing sustainability, businesses can harness the transformative power of cloud computing to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and achieve lasting success.
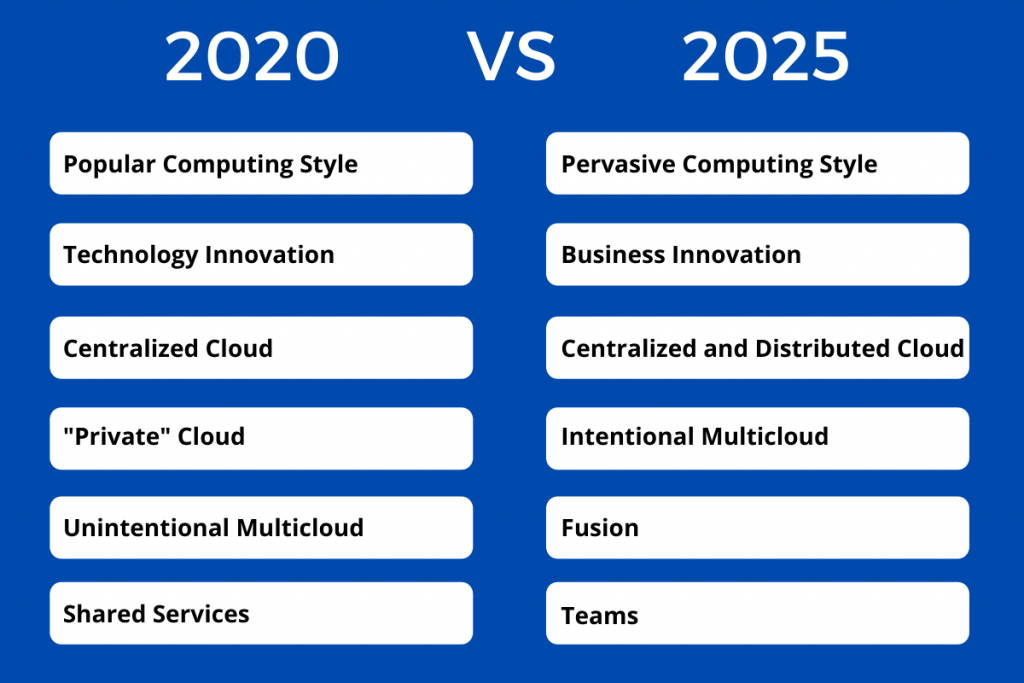






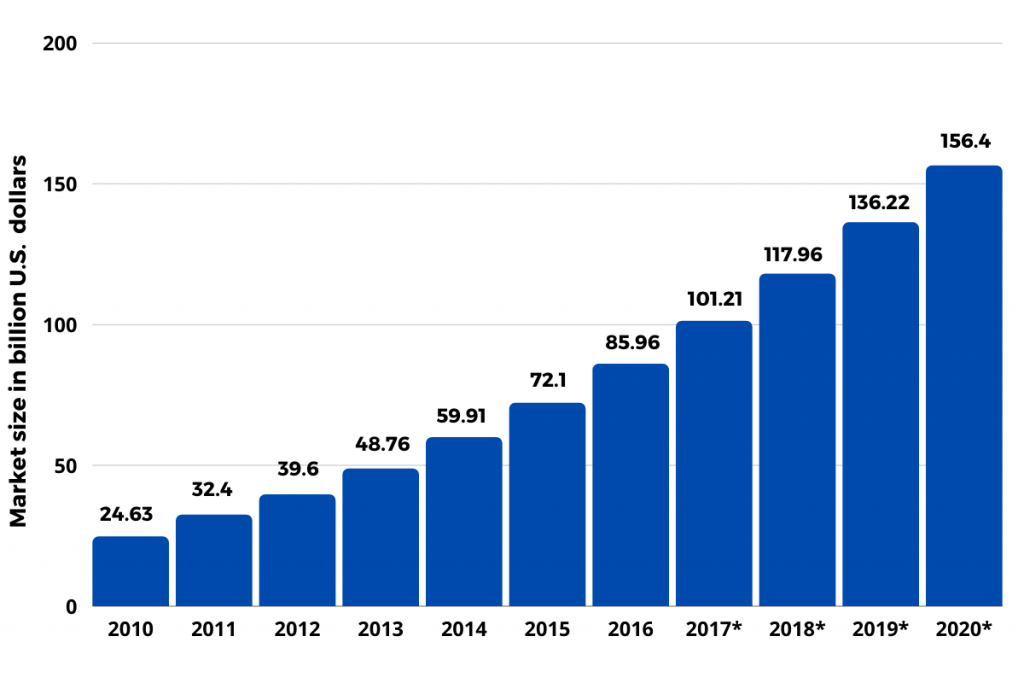
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolving Landscape of Cloud Computing: Trends Shaping 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!