The Evolving Landscape of the Internet of Things: Trends Shaping the Future by 2025
The Evolving Landscape of the Internet of Things: Trends Shaping the Future by 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Evolving Landscape of the Internet of Things: Trends Shaping the Future by 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolving Landscape of the Internet of Things: Trends Shaping the Future by 2025
The Internet of Things (IoT) has rapidly transformed from a futuristic concept to a ubiquitous reality, impacting industries and daily lives alike. As we approach 2025, the IoT landscape is poised for further evolution, driven by technological advancements, evolving user expectations, and the emergence of new applications. This exploration delves into the key trends shaping the future of the IoT, providing insights into its potential impact on various sectors and the broader societal landscape.
1. The Rise of Edge Computing and Decentralization
The sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices necessitates a shift from centralized cloud computing to edge computing. Edge computing brings processing and data analysis closer to the source, enabling faster response times, reduced latency, and improved data privacy. This trend is crucial for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring.
Benefits of Edge Computing:
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing minimizes the distance data travels, resulting in significantly faster processing and response times. This is critical for applications demanding real-time decision-making, such as self-driving cars and industrial control systems.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the need to transmit sensitive information to centralized servers, enhancing data privacy and security.
- Improved Reliability: Edge computing provides greater resilience to network outages and disruptions. If a central server fails, edge devices can continue to operate autonomously, ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Increased Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the volume of data transmitted to the cloud, optimizing network bandwidth usage.
2. The Convergence of IoT and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The integration of AI with the IoT unlocks new possibilities by enabling intelligent decision-making, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from IoT devices, identifying patterns, predicting future outcomes, and optimizing operations.
Applications of AI in IoT:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze sensor data from machinery to predict potential failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Smart Home Automation: AI-powered home assistants can learn user preferences and automate tasks like temperature control, lighting, and appliance usage.
- Personalized Healthcare: AI can analyze wearable sensor data to monitor patient health, detect anomalies, and provide personalized health recommendations.
- Smart City Management: AI can optimize traffic flow, manage energy consumption, and improve public safety by analyzing data from sensors deployed throughout the city.
3. The Growth of 5G and Beyond
The rollout of 5G and future generations of mobile networks will significantly impact the IoT by providing faster speeds, lower latency, and greater network capacity. This will facilitate the deployment of more complex IoT applications, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and virtual reality experiences.
Impact of 5G on IoT:
- Enhanced Connectivity: 5G offers significantly faster speeds and lower latency compared to previous generations of mobile networks, enabling real-time communication between IoT devices and the cloud.
- Increased Bandwidth: 5G provides greater bandwidth, allowing for the transmission of larger volumes of data from IoT devices. This is crucial for applications generating massive amounts of data, such as industrial sensors and smart cities.
- Improved Reliability: 5G networks are designed to be more resilient and reliable than previous generations, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity for mission-critical IoT applications.
- Support for Massive IoT: 5G networks can support a massive number of connected devices, enabling the deployment of large-scale IoT deployments in smart cities, factories, and other environments.
4. The Importance of Security and Privacy
As the number of connected devices grows, ensuring the security and privacy of IoT data becomes paramount. Cybersecurity threats targeting IoT devices are increasing, and robust measures are needed to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Security and Privacy Challenges in IoT:
- Vulnerabilities in Devices: Many IoT devices have limited security features, making them vulnerable to hacking and malware attacks.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The collection and storage of personal data from IoT devices raise significant privacy concerns, requiring strong safeguards to protect sensitive information.
- Lack of Standardization: The lack of standardized security protocols for IoT devices creates fragmentation and makes it difficult to implement consistent security measures.
- Complexity of Management: Managing security across a large number of interconnected devices can be challenging, requiring sophisticated security solutions and expertise.
5. The Growing Importance of Sustainability
The IoT plays a critical role in promoting sustainability by enabling energy efficiency, waste reduction, and resource optimization. Sustainable IoT solutions aim to minimize environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Sustainable IoT Applications:
- Smart Grid Management: IoT sensors can monitor energy consumption in homes and businesses, enabling real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage and reduce carbon emissions.
- Precision Agriculture: IoT sensors can monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, enabling farmers to optimize irrigation and fertilization, reducing water and fertilizer usage.
- Waste Management: Smart waste bins can monitor fill levels and alert collection services when they need to be emptied, optimizing waste collection routes and reducing transportation costs.
- Building Automation: IoT sensors can control lighting, heating, and ventilation systems in buildings, optimizing energy consumption and reducing energy bills.
6. The Rise of Blockchain in IoT
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for managing data in IoT systems. It enables secure data sharing, tamper-proof record keeping, and decentralized control, enhancing trust and transparency in IoT applications.
Applications of Blockchain in IoT:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of goods through the supply chain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Device Authentication: Blockchain can be used to authenticate IoT devices, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of data.
- Data Security: Blockchain provides a secure and tamper-proof ledger for storing IoT data, enhancing data security and protecting against unauthorized access.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate transactions and agreements between IoT devices, reducing the need for intermediaries and improving efficiency.
7. The Expansion of IoT in Healthcare
The IoT is transforming the healthcare industry by enabling remote patient monitoring, personalized medicine, and more efficient healthcare delivery. Telehealth solutions leverage IoT devices to connect patients with healthcare providers remotely, improving access to care and reducing costs.
Applications of IoT in Healthcare:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable sensors can track vital signs, activity levels, and medication adherence, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely.
- Personalized Medicine: IoT devices can collect data on patient health and lifestyle, enabling personalized treatment plans and preventive measures.
- Smart Hospitals: IoT sensors can monitor hospital environments, optimize resource allocation, and automate tasks, improving efficiency and patient care.
- Drug Delivery: IoT-enabled devices can monitor and control drug delivery, ensuring accurate dosage and reducing medication errors.
8. The Increasing Integration of IoT in Industries
The IoT is revolutionizing industries by enabling automation, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced efficiency. Industrial IoT (IIoT) solutions connect machines, sensors, and other industrial equipment, providing real-time insights into operations and optimizing production processes.
Applications of IIoT:
- Predictive Maintenance: IIoT sensors can monitor equipment performance, identifying potential failures and enabling proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
- Process Optimization: IIoT data can be used to optimize production processes, improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing quality.
- Remote Monitoring: IIoT enables remote monitoring of industrial operations, allowing for real-time insights and control, regardless of location.
- Supply Chain Management: IIoT can track the movement of goods through the supply chain, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
Related Searches
1. Future of IoT: This topic explores the long-term trends and potential impact of the IoT on various industries and aspects of society. It examines emerging technologies, potential applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding the widespread adoption of IoT.
2. IoT Trends 2023: This focuses on the current trends and advancements in the IoT, highlighting the most recent developments and their implications for businesses and individuals.
3. Impact of IoT on Society: This examines the broader societal impact of the IoT, including its influence on employment, privacy, security, and the future of work.
4. IoT Applications: This delves into the various applications of the IoT across different industries, providing examples and case studies of successful implementations.
5. IoT Security: This focuses on the security challenges and vulnerabilities associated with IoT devices and networks, exploring best practices for protecting sensitive information and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
6. IoT Business Models: This explores the various business models emerging in the IoT space, including device manufacturers, service providers, and data analytics platforms.
7. IoT Ecosystem: This examines the interconnectedness of different components within the IoT ecosystem, including hardware, software, networks, and data analytics tools.
8. IoT Standards: This focuses on the development and implementation of standards for IoT devices and networks, promoting interoperability and ensuring compatibility between different systems.
FAQs by Trends in IoT 2025:
1. What are the key challenges facing the widespread adoption of the IoT?
- Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of IoT data is a critical challenge, requiring robust security measures and data protection protocols.
- Interoperability: The lack of standardized protocols for IoT devices can create interoperability issues, hindering the seamless integration of different systems.
- Cost and Complexity: Implementing and managing large-scale IoT deployments can be expensive and complex, requiring specialized expertise and infrastructure.
- Data Management: Handling the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices requires efficient data management and analytics capabilities.
- Regulatory Landscape: The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding IoT devices and data privacy can create challenges for businesses and developers.
2. How will the IoT impact the future of work?
- Automation of Tasks: The IoT will automate many tasks currently performed by humans, leading to job displacement in some areas but creating new opportunities in others.
- Increased Efficiency: The IoT will enhance efficiency and productivity in various industries, requiring a skilled workforce to manage and maintain complex IoT systems.
- Remote Work: The IoT will enable remote work and collaboration, expanding opportunities for individuals in geographically diverse locations.
- New Skills and Roles: The IoT will create new job roles related to data analytics, cybersecurity, and IoT system design and maintenance.
3. What are the ethical implications of the IoT?
- Data Privacy: The collection and use of personal data from IoT devices raise concerns about data privacy and the potential for misuse.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI algorithms used in IoT applications can perpetuate existing biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks through the IoT could lead to widespread job displacement, raising concerns about economic inequality.
- Surveillance: The proliferation of IoT sensors and cameras raises concerns about increased surveillance and the potential for privacy violations.
Tips by Trends in IoT 2025:
- Embrace Edge Computing: Businesses should explore edge computing solutions to address the challenges of data volume and latency in IoT applications.
- Integrate AI: Incorporating AI into IoT systems can unlock new possibilities for intelligent decision-making and predictive analytics.
- Prioritize Security: Implement robust security measures to protect IoT devices and data from cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
- Promote Sustainability: Design and deploy IoT solutions that minimize environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Embrace Standardization: Advocate for the development and adoption of standardized protocols for IoT devices and networks to enhance interoperability.
Conclusion by Trends in IoT 2025:
The Internet of Things is poised to continue its transformative journey, shaping industries, enhancing daily life, and driving innovation across various sectors. The trends outlined in this exploration highlight the dynamic evolution of the IoT, emphasizing the importance of security, privacy, sustainability, and the integration of emerging technologies. As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, understanding these trends is essential for businesses, individuals, and policymakers alike to navigate this exciting and ever-changing technological landscape.
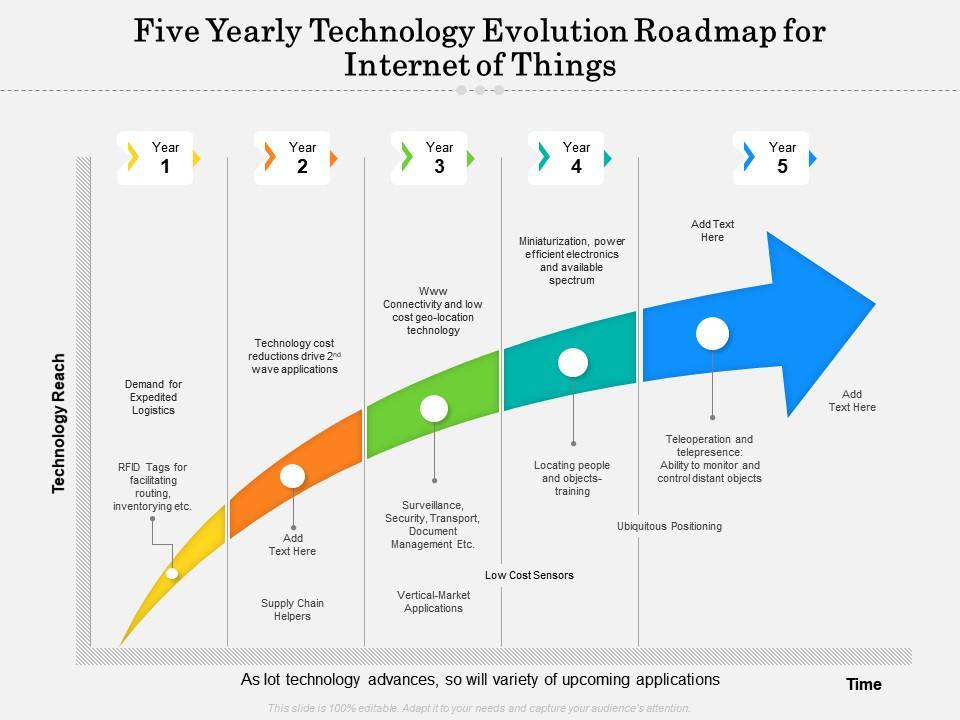
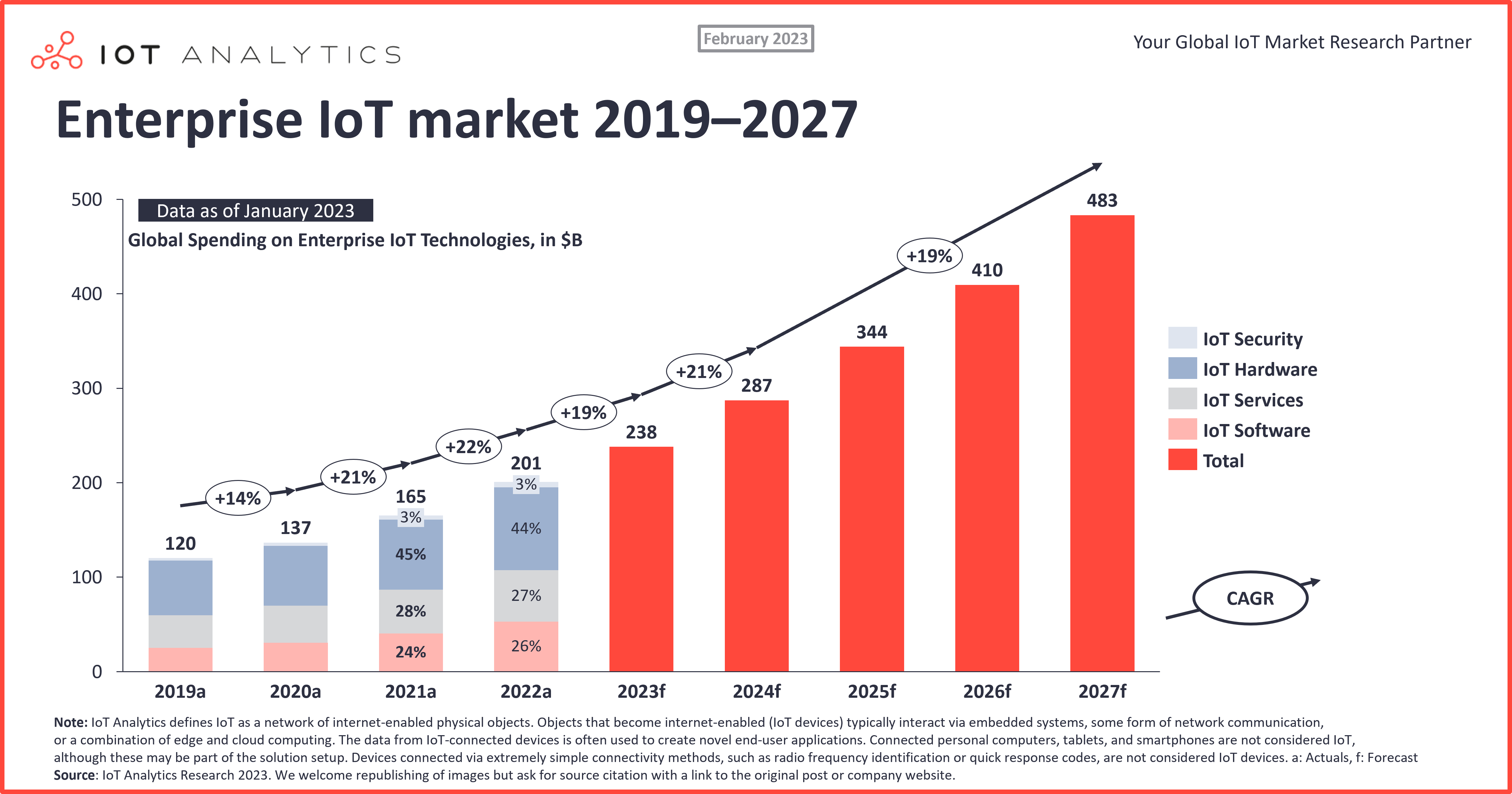
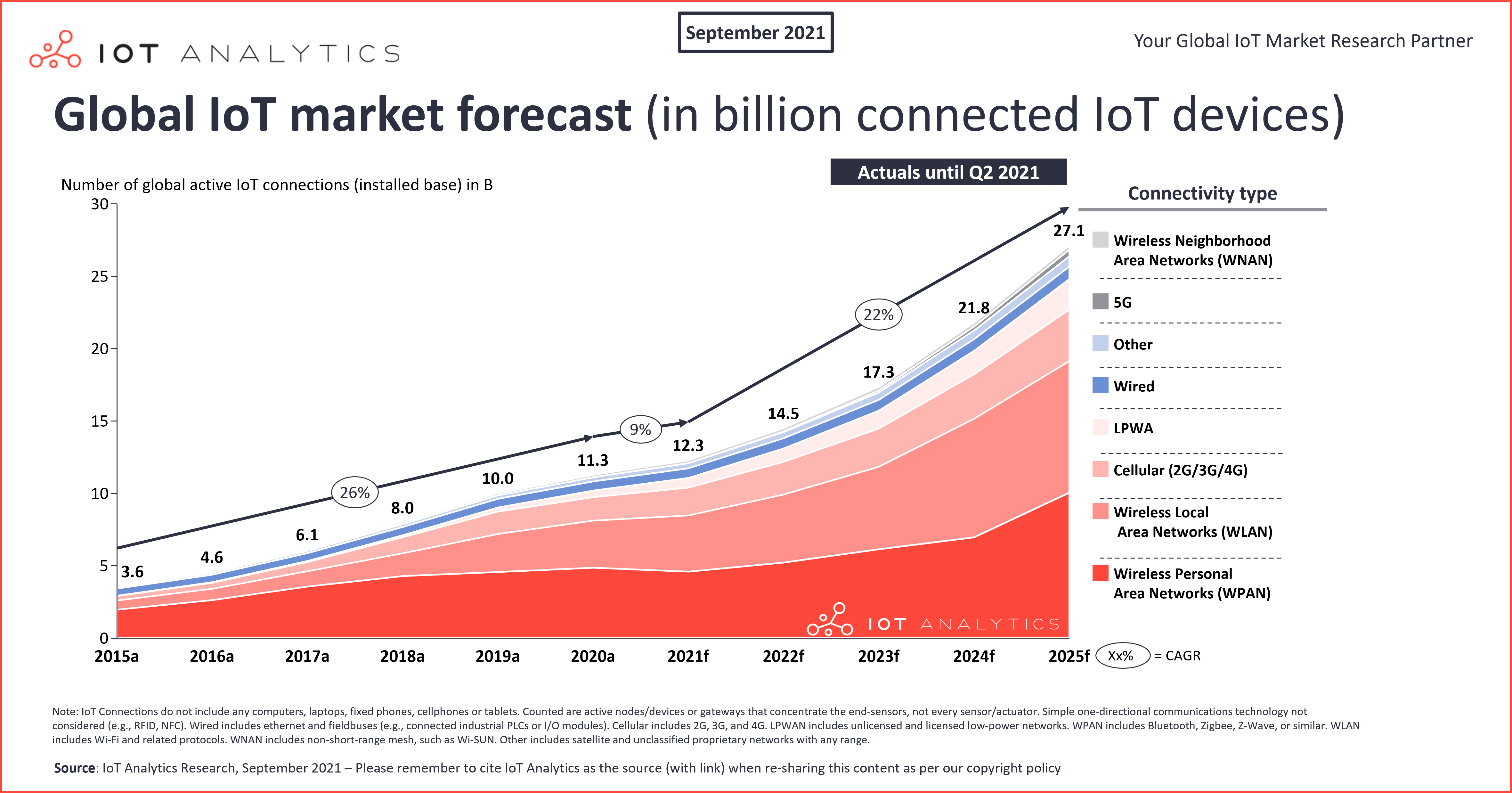

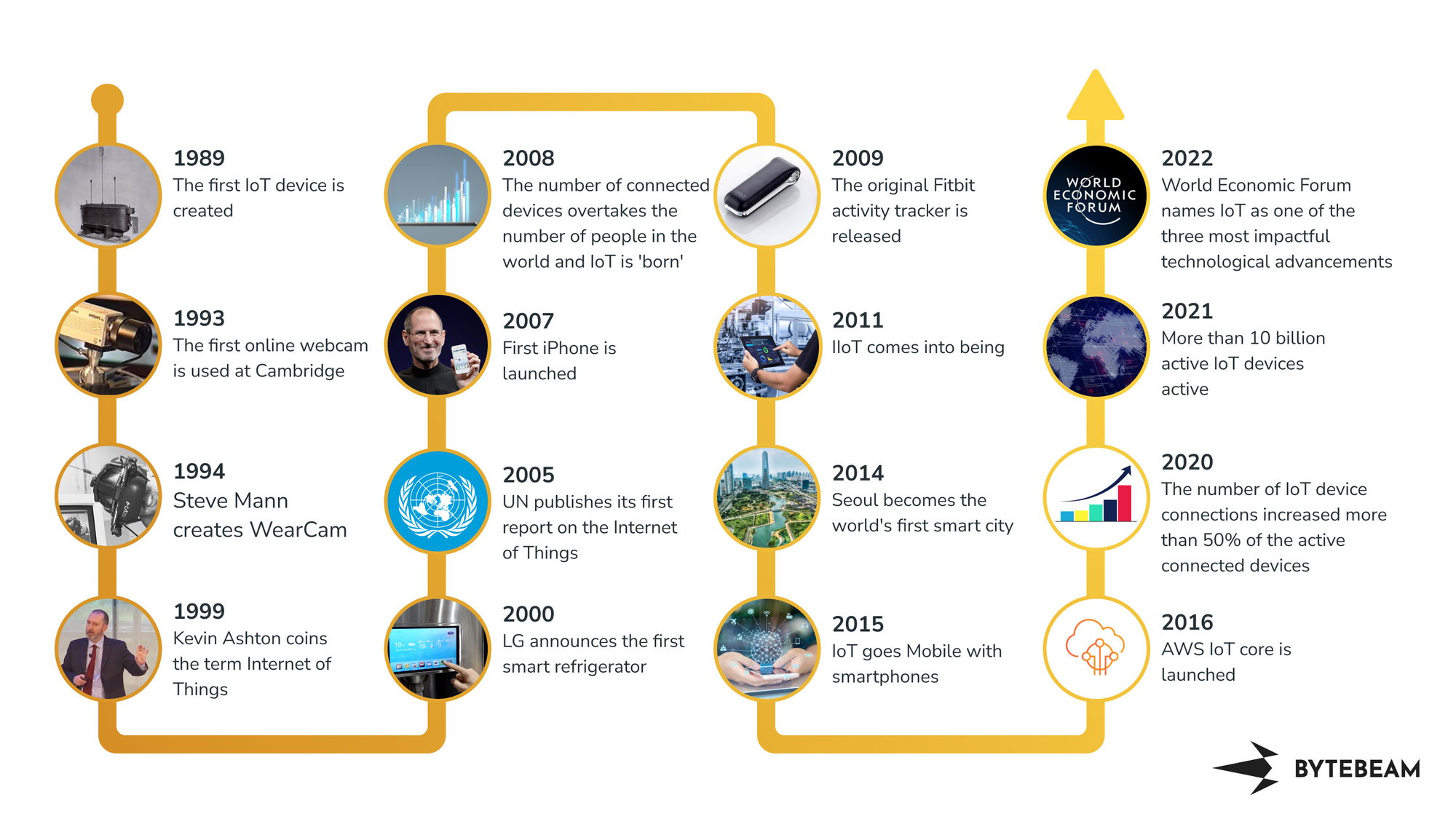
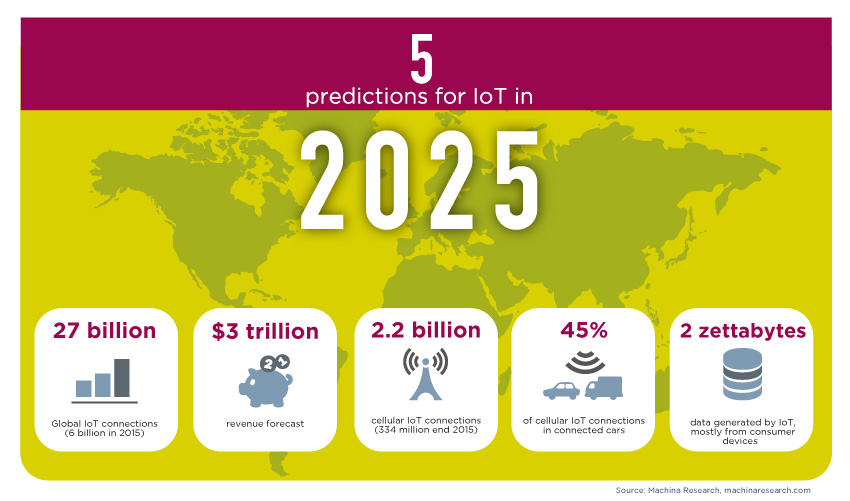
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolving Landscape of the Internet of Things: Trends Shaping the Future by 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
