Understanding the Shifting Landscape: Demographics Trends in 2025 and Beyond
Understanding the Shifting Landscape: Demographics Trends in 2025 and Beyond
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Shifting Landscape: Demographics Trends in 2025 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Shifting Landscape: Demographics Trends in 2025 and Beyond
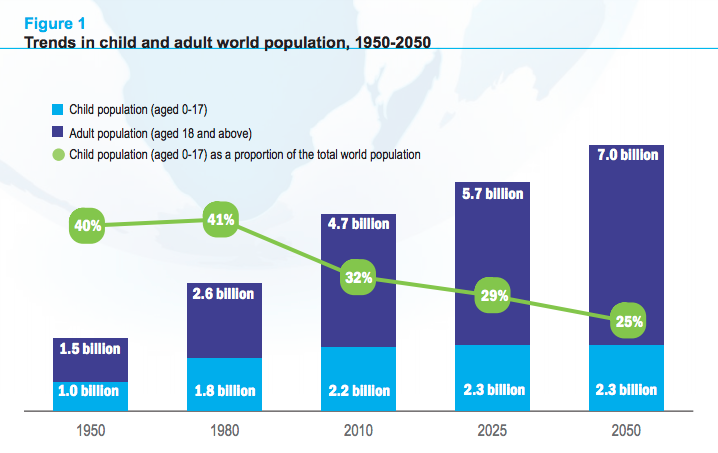
The world is in constant flux, and understanding the forces driving this change is crucial for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. Demographics trends are a key driver of this change, revealing the evolving composition of populations in terms of age, gender, ethnicity, education, income, and other factors. These trends are not merely interesting data points; they shape the future of societies, economies, and even individual lives.
Looking ahead to 2025, we see a landscape marked by significant demographic shifts with profound implications. This article delves into the key trends shaping the world in the coming years, exploring their impact on various aspects of life.
Key Demographic Trends Shaping 2025:
1. Aging Populations:
The world is getting older. Life expectancy is rising globally, while birth rates are declining in many regions. This leads to a growing proportion of older adults, with implications for healthcare systems, retirement planning, and social structures.
- Impact: Increased demand for healthcare services, particularly long-term care; strain on social security and pension systems; potential labor shortages as older workers retire; rising demand for age-friendly products and services; shift in consumer preferences towards health and wellness.
2. Urbanization:
The global population is increasingly concentrated in urban areas. This trend is driven by factors such as economic opportunities, access to services, and social mobility.
- Impact: Growing demand for housing, transportation, and infrastructure in cities; challenges in managing urban sprawl and environmental impact; opportunities for innovation in urban planning and technology; potential for social and economic inequality within cities.
3. Population Growth and Distribution:
While global population growth is slowing down, it continues to rise, particularly in developing countries. This growth is unevenly distributed, with certain regions experiencing rapid population increases while others are facing population decline.
- Impact: Strain on resources and infrastructure in rapidly growing regions; potential for conflict over resources; opportunities for economic growth and development in areas with growing populations; challenges in managing migration and displacement.
4. Education and Skills:
The global workforce is becoming more educated and skilled. This is driven by increased access to education and changing demands of the labor market.
- Impact: Higher productivity and innovation; potential for economic growth and development; challenges in adapting education systems to meet evolving skills needs; potential for skills gaps and unemployment.
5. Diversity and Inclusion:
Societies are becoming more diverse, with increasing representation of different ethnicities, religions, and cultures. This trend is driven by globalization, migration, and changing social attitudes.
- Impact: Opportunities for cultural enrichment and economic growth; challenges in promoting social cohesion and addressing discrimination; potential for greater tolerance and understanding; need for policies and practices that promote inclusivity.
6. Digital Transformation:
The rise of digital technologies is transforming the way people live, work, and interact with the world. This trend is impacting demographics through increased access to information, education, and services.
- Impact: Increased opportunities for education, employment, and social connection; challenges in bridging the digital divide; potential for social isolation and mental health issues; need for digital literacy skills and ethical frameworks for technology use.
7. Changing Family Structures:
Traditional family structures are evolving, with increasing numbers of single-parent households, blended families, and childless couples. This trend is driven by factors such as delayed marriage, increased divorce rates, and changing social norms.
- Impact: Challenges in providing support for non-traditional families; potential for social and economic inequality; opportunities for innovation in family-friendly policies and services; need for greater understanding and acceptance of diverse family structures.
8. Climate Change and Environmental Impact:
Climate change and environmental degradation are impacting demographics through displacement, migration, and health issues. This trend is expected to intensify in the coming years.
- Impact: Challenges in managing climate-related displacement and migration; potential for conflict over resources; need for adaptation strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change; opportunities for innovation in sustainable technologies and practices.
Exploring Related Searches:
Understanding these trends requires exploring related searches that delve deeper into specific aspects of demographic change:
1. Global Population Growth:
- Population Pyramids: Visual representations of age and gender distribution within a population, providing insights into population structure and future trends.
- Fertility Rates: The average number of children born per woman, a key indicator of population growth and aging.
- Life Expectancy: The average number of years a person is expected to live, influenced by factors such as healthcare, nutrition, and lifestyle.
2. Urbanization Trends:
- Mega-cities: Cities with populations exceeding 10 million, experiencing rapid growth and posing unique challenges for urban planning and infrastructure.
- Urban Sprawl: The outward expansion of urban areas into surrounding rural areas, leading to environmental degradation and social isolation.
- Smart Cities: Cities utilizing technology to improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life for residents.
3. Migration Patterns:
- International Migration: Movement of people across national borders, driven by factors such as economic opportunities, conflict, and climate change.
- Internal Migration: Movement of people within a country, often from rural areas to urban centers.
- Refugee Crisis: The displacement of people forced to flee their homes due to conflict, persecution, or natural disasters.
4. Education and Skills Gap:
- Higher Education Enrollment: The proportion of the population enrolled in tertiary education, indicating the level of educational attainment.
- Skills Mismatch: The gap between the skills required by employers and the skills possessed by the workforce, leading to unemployment and underemployment.
- STEM Education: Focus on education in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, crucial for technological advancement and economic competitiveness.
5. Diversity and Inclusion:
- Ethnic Diversity: The representation of different ethnic groups within a population, contributing to cultural richness and social dynamism.
- Religious Diversity: The presence of different religious beliefs and practices within a society, promoting tolerance and understanding.
- Gender Equality: The equal rights and opportunities for women and men in all aspects of life, contributing to economic growth and social progress.
6. Digital Divide:
- Internet Access: The availability and affordability of internet access for all members of society, essential for participation in the digital economy.
- Digital Literacy: The ability to effectively use digital technologies and information, essential for navigating the digital world.
- Cybersecurity: The protection of digital systems and information from unauthorized access and cyberattacks, crucial for ensuring trust and security in the digital age.
7. Family Structures and Social Change:
- Marriage Rates: The proportion of the population that is married, reflecting changing social norms and attitudes towards marriage.
- Divorce Rates: The proportion of marriages that end in divorce, indicating changing family structures and societal values.
- Childlessness: The increasing number of couples choosing not to have children, driven by factors such as career aspirations and financial constraints.
8. Climate Change and Environmental Impact:
- Sea Level Rise: The gradual increase in global sea levels due to melting glaciers and thermal expansion, threatening coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Extreme Weather Events: The increasing frequency and intensity of storms, droughts, and heat waves, impacting human health, agriculture, and infrastructure.
- Environmental Migration: The movement of people forced to relocate due to climate change impacts, such as desertification, flooding, and extreme weather events.
FAQs by Demographics Trends Definition 2025:
Q: What is the significance of demographics trends for businesses?
A: Understanding demographics trends is vital for businesses to adapt their products, services, and marketing strategies to meet the evolving needs and preferences of their target audience. This includes tailoring products to specific age groups, addressing the needs of diverse communities, and utilizing digital channels to reach consumers effectively.
Q: How can governments leverage demographics trends for policymaking?
A: Governments can utilize demographics trends to inform policy decisions in areas such as healthcare, education, social security, and infrastructure development. This includes investing in healthcare systems to meet the needs of an aging population, adapting education systems to prepare young people for the future workforce, and investing in sustainable infrastructure to address climate change impacts.
Q: What are the potential challenges associated with demographics trends?
A: While demographics trends offer opportunities for growth and development, they also present challenges. These include managing aging populations, addressing social inequalities, mitigating the impacts of climate change, and ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities for all members of society.
Q: How can individuals prepare for the demographic changes ahead?
A: Individuals can prepare for demographic changes by staying informed about key trends, developing skills that are in demand, adapting to changing work environments, and engaging in responsible consumption practices. This includes investing in lifelong learning, embracing digital technologies, and making conscious choices that support sustainability and social justice.
Tips by Demographics Trends Definition 2025:
- Stay informed: Regularly engage with data and analysis on demographics trends to understand the evolving landscape and its implications.
- Embrace diversity: Promote inclusivity and understanding in all aspects of life, recognizing the value of diverse perspectives and experiences.
- Develop future-proof skills: Invest in education and training to acquire skills that are in demand in the evolving job market.
- Adapt to changing work environments: Be flexible and adaptable to new technologies, work models, and collaborative approaches.
- Engage in responsible consumption: Make conscious choices that support sustainability, social justice, and ethical business practices.
Conclusion by Demographics Trends Definition 2025:
Demographics trends are not static phenomena; they are dynamic forces shaping the world around us. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments to navigate the future effectively. By embracing the opportunities and addressing the challenges presented by these trends, we can create a more equitable, sustainable, and prosperous world for all.


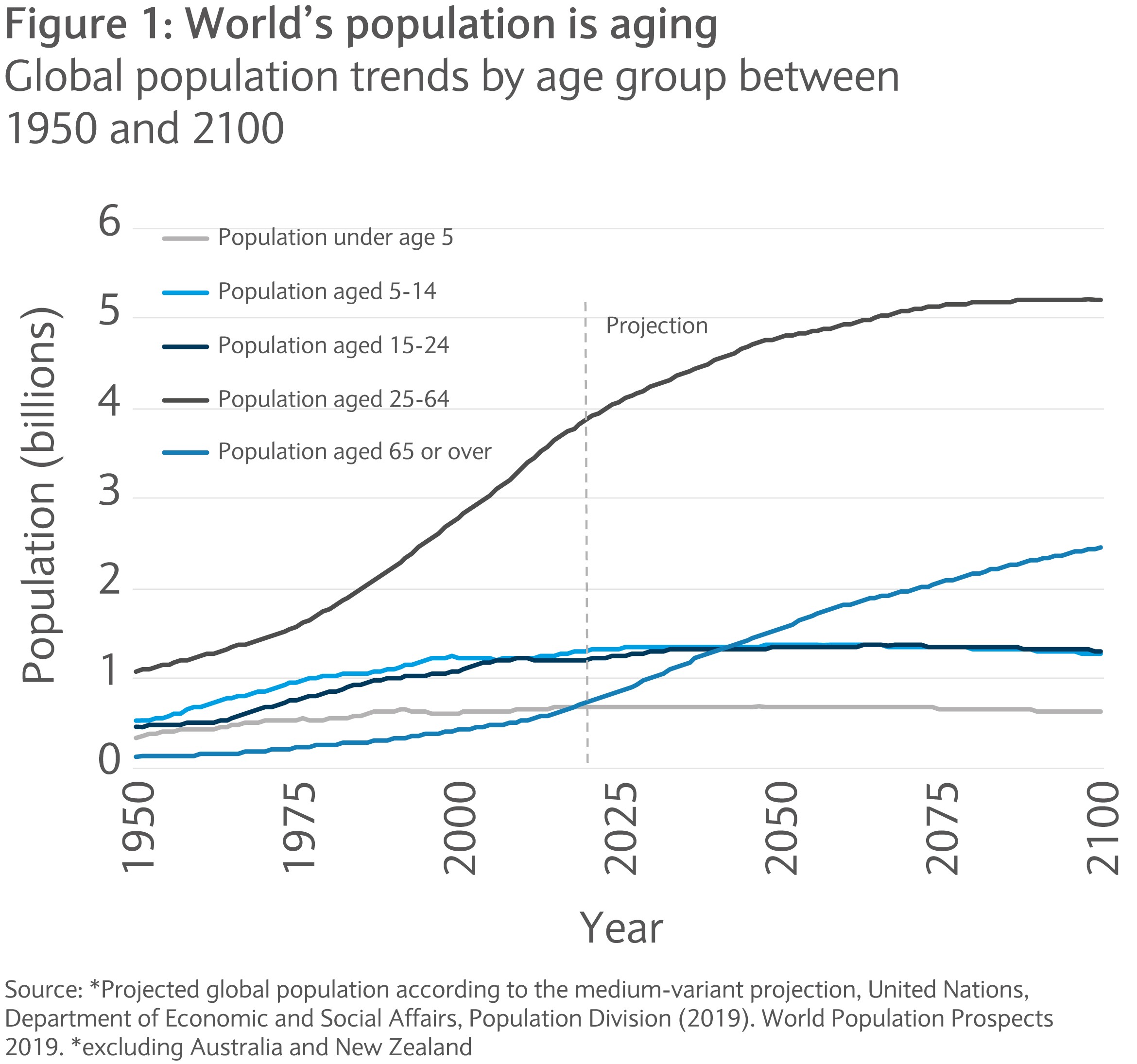



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Shifting Landscape: Demographics Trends in 2025 and Beyond. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!