Unpacking the Shifting Landscape: Demographic Trends Shaping the World by 2025
Unpacking the Shifting Landscape: Demographic Trends Shaping the World by 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Shifting Landscape: Demographic Trends Shaping the World by 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Shifting Landscape: Demographic Trends Shaping the World by 2025

The world is in constant flux, and understanding the forces driving change is crucial for navigating the future. Demographic trends are one such driving force, shaping everything from economic growth and political landscapes to social structures and cultural shifts. By 2025, a confluence of factors will have profoundly altered the global demographic picture, presenting both opportunities and challenges for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
Definition of Demographic Trends 2025
ItalicDemographic trends italic refer to the long-term patterns of change in population characteristics such as age, gender, ethnicity, education, income, and geographic location. These trends are not static but evolve over time, influenced by a complex interplay of factors like birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, and social and economic development. Understanding these shifts is essential for informed decision-making in various sectors, from healthcare and education to marketing and policy development.*
Key Demographic Trends Shaping the World by 2025
1. Aging Populations:
The global population is aging, with a growing proportion of older adults. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed countries, where life expectancy is increasing and birth rates are declining. By 2025, the number of people aged 65 and over will surpass the number of children under five for the first time in history.
-
Implications:
- Healthcare Systems: Aging populations will place increasing pressure on healthcare systems, requiring investment in long-term care facilities, geriatric services, and chronic disease management.
- Labor Markets: The shrinking workforce will require strategies to address labor shortages, including attracting and retaining older workers, promoting immigration, and investing in automation and technology.
- Economic Growth: Aging populations can lead to slower economic growth, as consumer spending declines and innovation slows.
2. Population Growth and Urbanization:
While the global population is growing, the rate of growth is slowing down. However, significant population growth is expected in developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia. This growth, coupled with urbanization, will lead to increasing pressure on resources, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability.
-
Implications:
- Resource Management: Sustainable resource management will become increasingly critical, including water, energy, and food.
- Urban Planning: Cities will need to invest in efficient transportation systems, affordable housing, and public services to accommodate growing populations.
- Environmental Impacts: Urbanization and population growth will exacerbate environmental problems such as air pollution, water scarcity, and climate change.
3. Changing Family Structures:
Family structures are evolving globally, with rising rates of single-person households, cohabitation, and delayed marriage and childbirth. This shift has implications for social support networks, childcare arrangements, and housing needs.
-
Implications:
- Social Support: Governments and communities will need to address the changing needs of individuals and families, providing support for single parents, older adults living alone, and other non-traditional family arrangements.
- Work-Life Balance: Flexible work arrangements and affordable childcare will become increasingly important for individuals balancing work and family responsibilities.
- Housing Markets: The demand for smaller and more affordable housing options will increase, particularly in urban areas.
4. Education and Skills Gap:
The global workforce is becoming increasingly skilled and educated. However, there is a growing skills gap, with a mismatch between the skills employers need and the skills available in the workforce. This gap is exacerbated by technological advancements and automation, which are transforming the nature of work.
-
Implications:
- Education Systems: Education systems need to adapt to the changing demands of the labor market, providing students with the skills and knowledge necessary for success in a rapidly evolving economy.
- Workforce Development: Investment in training and reskilling programs will be crucial to bridge the skills gap and equip workers with the skills needed for the jobs of the future.
- Economic Competitiveness: Addressing the skills gap is essential for maintaining economic competitiveness and fostering innovation.
5. Global Migration and Diversity:
Migration patterns are changing, with increasing flows of people from developing to developed countries. This migration is driven by factors such as economic opportunities, political instability, and climate change. The growing diversity of populations will reshape societies and create new challenges and opportunities.
-
Implications:
- Social Integration: Policies and programs will be needed to promote social integration and inclusion of immigrants, fostering a sense of belonging and reducing tensions.
- Cultural Exchange: Increased diversity can lead to cultural enrichment and innovation, but it also requires understanding and respect for different cultures and values.
- Labor Markets: Immigration can contribute to economic growth by filling labor shortages, but it also raises concerns about wages, job displacement, and social services.
Understanding the Importance of Demographic Trends
ItalicDemographic trends italic are not merely statistical data points; they are powerful forces shaping the future of our world. Understanding these trends is crucial for:
- Informed Policy Making: Governments can use demographic data to inform policy decisions related to healthcare, education, social welfare, and economic development.
- Business Strategy: Businesses can leverage demographic insights to target their products and services, develop marketing campaigns, and make strategic investments.
- Social Planning: Community organizations and non-profits can use demographic data to understand the needs of their communities and design programs to address social challenges.
- Individual Planning: Individuals can use demographic trends to make informed decisions about their careers, education, and financial planning.
Related Searches: Exploring Further Insights
1. Demographic Trends by Region:
- Europe: Aging population, declining birth rates, increasing immigration.
- North America: Aging population, moderate population growth, increasing diversity.
- Asia: Rapid population growth, urbanization, aging population in some countries.
- Africa: High birth rates, rapid population growth, urbanization.
- Latin America: Moderate population growth, urbanization, aging population in some countries.
2. Impact of Technology on Demographic Trends:
- Automation and Robotics: These technologies are expected to impact labor markets, potentially displacing some jobs but creating new opportunities in other sectors.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI has the potential to transform healthcare, education, and other sectors, influencing demographic trends by changing how people live, work, and age.
- Digital Communication: Social media and other digital platforms are shaping social interactions and influencing migration patterns.
3. Global Aging and its Implications:
- Healthcare Costs: Rising healthcare costs associated with chronic diseases and long-term care are a major concern for aging societies.
- Social Security Systems: The sustainability of social security systems is under pressure due to aging populations and declining birth rates.
- Intergenerational Equity: The increasing burden of supporting aging populations raises questions about intergenerational equity and the distribution of resources.
4. Urbanization and its Challenges:
- Sustainable Cities: Cities need to become more sustainable to accommodate growing populations while minimizing environmental impacts.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in transportation, housing, and public services are crucial for managing urban growth.
- Social Inclusion: Urban planning needs to address issues of inequality and social exclusion to create inclusive and equitable cities.
5. Migration and its Impacts:
- Refugee Crises: Global conflicts and climate change are leading to increased refugee flows, presenting challenges for receiving countries.
- Brain Drain: Migration of skilled workers from developing countries can lead to a loss of talent and economic potential.
- Integration Policies: Effective integration policies are essential for fostering social cohesion and promoting economic growth.
6. Population Growth and its Environmental Impacts:
- Resource Depletion: Growing populations put pressure on natural resources such as water, energy, and land.
- Climate Change: Population growth contributes to climate change through increased emissions and resource consumption.
- Biodiversity Loss: Habitat loss and pollution associated with population growth threaten biodiversity.
7. Education and Skills Development:
- STEM Education: Demand for STEM skills is growing rapidly due to technological advancements.
- Lifelong Learning: Individuals will need to continuously learn and adapt to changing job markets.
- Vocational Training: Investment in vocational training programs is essential for preparing workers for in-demand jobs.
8. Gender Equality and its Role in Demographic Trends:
- Women’s Education and Empowerment: Investing in women’s education and empowerment can lead to lower birth rates, improved health outcomes, and increased economic growth.
- Gender-Based Violence: Addressing gender-based violence is essential for promoting women’s health and well-being.
- Equal Opportunities: Creating equal opportunities for women in education, employment, and political participation is crucial for achieving sustainable development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Demographic Trends 2025
1. How are demographic trends measured?
Demographic trends are measured through various data sources, including censuses, surveys, vital statistics (births, deaths, marriages), and migration records. These data are analyzed to identify patterns and trends over time.
2. What are the key factors driving demographic trends?
Key factors driving demographic trends include birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, social and economic development, and technological advancements.
3. How do demographic trends impact economic growth?
Demographic trends can impact economic growth in various ways. For example, aging populations can lead to slower growth due to declining consumer spending and labor shortages. However, population growth and urbanization can also stimulate economic activity by creating new markets and opportunities.
4. What are the challenges and opportunities associated with aging populations?
Challenges include increasing healthcare costs, labor shortages, and the sustainability of social security systems. Opportunities include the potential for older workers to contribute to the economy and the growth of industries catering to the needs of older adults.
5. How can governments respond to demographic trends?
Governments can respond to demographic trends by implementing policies to address healthcare needs, promote economic growth, manage migration, and invest in education and workforce development.
Tips for Navigating Demographic Trends
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest demographic trends and their implications for your industry, community, and personal life.
- Embrace Change: Be adaptable and open to change, recognizing that demographic shifts will require adjustments in how we live, work, and interact with each other.
- Invest in Education and Skills Development: Invest in education and training to acquire the skills needed for the jobs of the future.
- Promote Social Inclusion: Work to promote social inclusion and reduce inequality, ensuring that everyone benefits from the opportunities presented by demographic changes.
- Foster Sustainable Development: Support policies and practices that promote sustainable development, ensuring that future generations have the resources they need to thrive.
Conclusion
ItalicDemographic trends italic are a powerful force shaping the future of our world. Understanding these trends is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities they present. By embracing change, investing in education and skills development, promoting social inclusion, and fostering sustainable development, we can create a future that is more equitable, prosperous, and resilient for all.
Note: This comprehensive article provides a starting point for understanding demographic trends in 2025. Further research and exploration of specific regions, industries, and social issues are encouraged to gain a deeper understanding of this dynamic and impactful area.



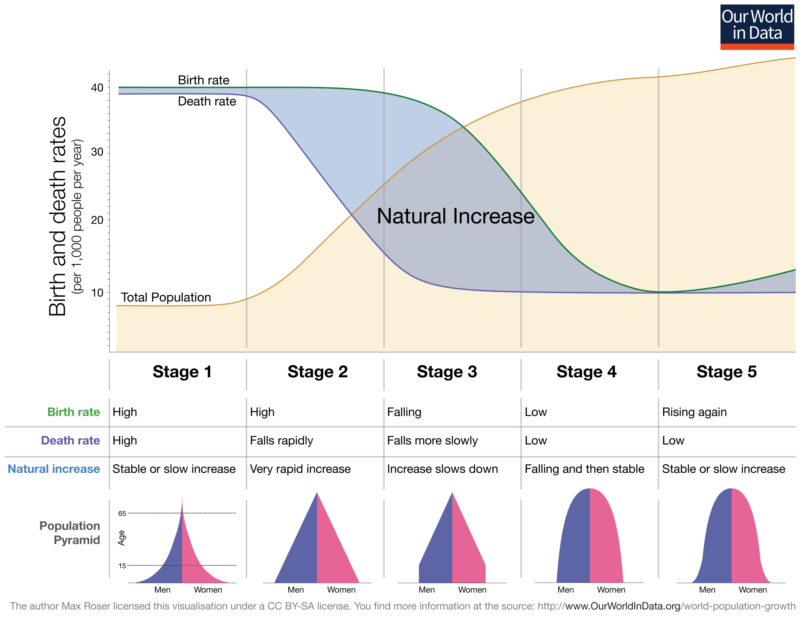
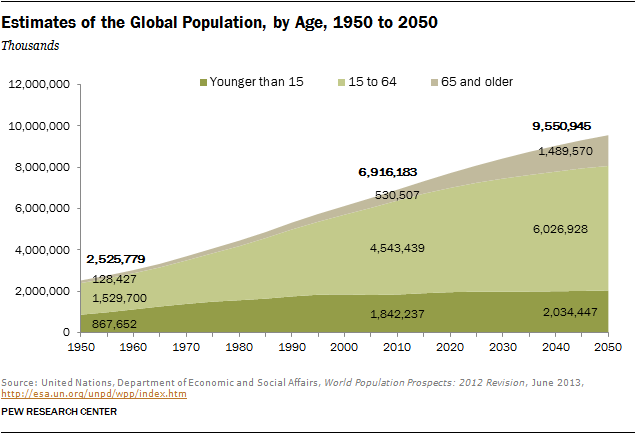
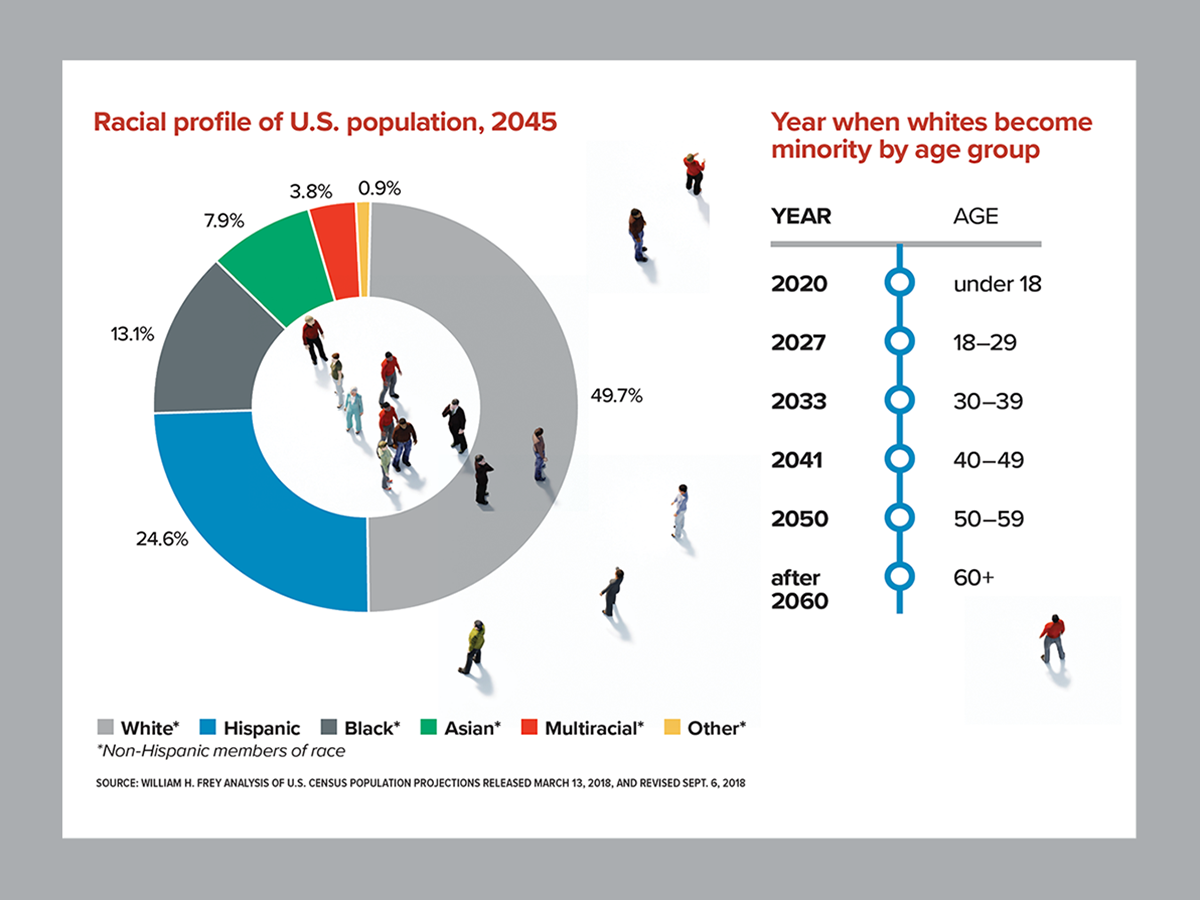
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Shifting Landscape: Demographic Trends Shaping the World by 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
