Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table
Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table
- 3.1 Delving into the Essence of Lattice Energy
- 3.2 Unveiling the Trends: A Periodic Table Perspective
- 3.3 Navigating the Periodic Table: A Visual Guide to Lattice Energy Trends
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Factors Influencing Lattice Energy
- 3.5 Applications of Lattice Energy: Unlocking Chemical Insights
- 3.6 Related Searches: Expanding the Knowledge Base
- 3.7 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.8 Tips for Understanding Lattice Energy Trends
- 3.9 Conclusion: Illuminating the Importance of Lattice Energy
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, organizes elements based on their recurring properties. This organization reveals fascinating trends, one of which is lattice energy. Lattice energy, a measure of the strength of the electrostatic interactions within a crystal lattice, plays a crucial role in understanding the stability and reactivity of ionic compounds.
Delving into the Essence of Lattice Energy
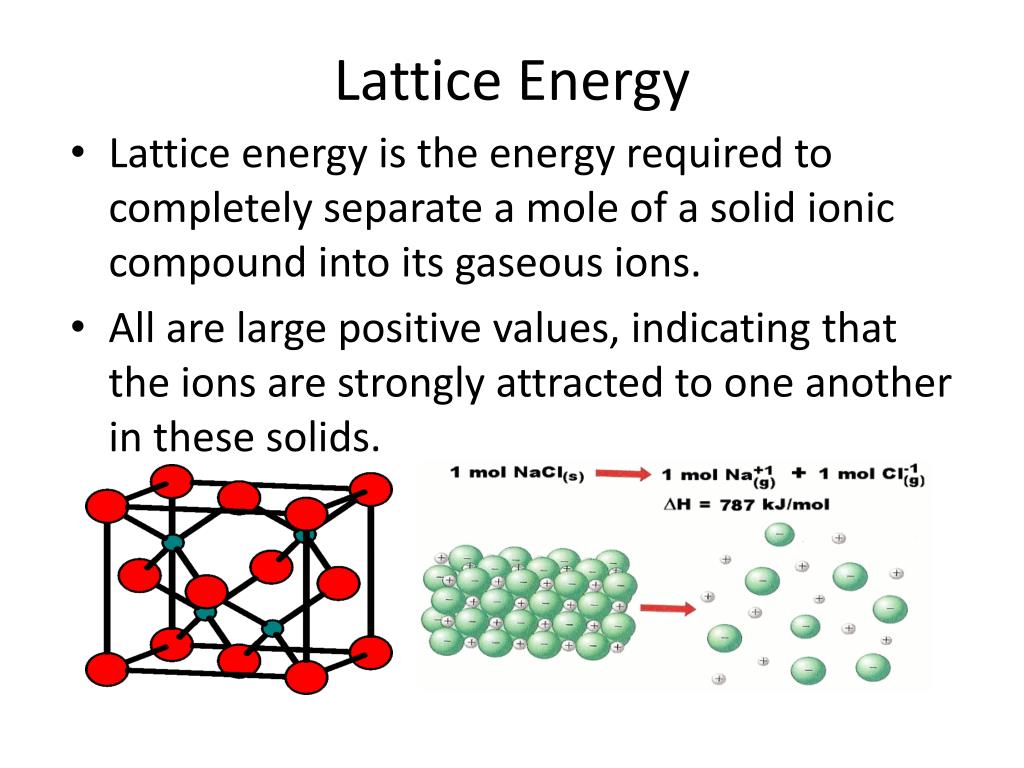
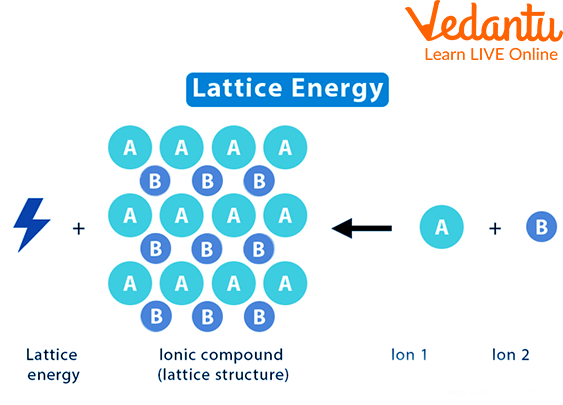
Lattice energy refers to the energy released when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions. It represents the strength of the electrostatic forces holding the ions together in the crystal lattice. Higher lattice energy indicates stronger ionic bonds, resulting in a more stable compound.
Imagine a crystal lattice as a tightly packed arrangement of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. These opposite charges attract each other, creating a strong electrostatic force that holds the crystal structure together. Lattice energy quantifies the strength of this attraction.
Unveiling the Trends: A Periodic Table Perspective
Understanding lattice energy trends on the periodic table requires considering two key factors:
-
Ionic Charge: As the charge of the ions increases, the electrostatic attraction between them strengthens, leading to higher lattice energy. For instance, magnesium oxide (MgO) has a higher lattice energy than sodium chloride (NaCl) due to the greater charges of Mg²⁺ and O²⁻ ions compared to Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
-
Ionic Size: Smaller ions experience stronger electrostatic forces due to their closer proximity. This leads to higher lattice energy for smaller ions. For example, lithium fluoride (LiF) has a higher lattice energy than potassium iodide (KI) because Li⁺ and F⁻ ions are smaller than K⁺ and I⁻ ions, respectively.
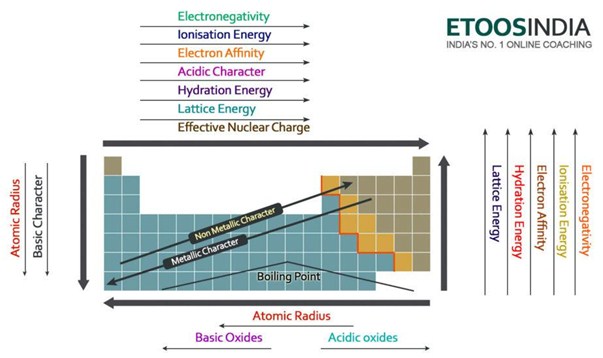
Navigating the Periodic Table: A Visual Guide to Lattice Energy Trends
Lattice energy trends can be visualized by moving across and down the periodic table:
Across a Period: As you move from left to right across a period, the ionic charge increases, leading to a general increase in lattice energy. However, ionic size also decreases across a period, which can partially counteract the effect of increasing charge.
Down a Group: Moving down a group, the ionic charge remains constant, but ionic size increases. This results in a decrease in lattice energy as the electrostatic attraction weakens with increasing distance between ions.
Beyond the Basics: Factors Influencing Lattice Energy
While ionic charge and size are the primary determinants of lattice energy, other factors can also influence its value:
-
Crystal Structure: Different crystal structures can influence the arrangement of ions and thus affect the strength of electrostatic interactions. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) has a face-centered cubic structure, while cesium chloride (CsCl) has a simple cubic structure. These structural differences can lead to variations in lattice energy.
-
Polarizability: Ions with larger electron clouds are more easily distorted by the electric field of neighboring ions. This polarizability effect can increase the attractive forces between ions, leading to higher lattice energy.
Applications of Lattice Energy: Unlocking Chemical Insights
Lattice energy plays a vital role in various chemical processes and applications:
-
Solubility: Compounds with high lattice energy are generally less soluble in water because the strong electrostatic interactions within the crystal lattice are difficult to overcome by the water molecules.
-
Reactivity: Compounds with high lattice energy are often less reactive due to the strong ionic bonds holding the ions together.
-
Thermochemical Calculations: Lattice energy is crucial for calculating enthalpy changes in various reactions involving ionic compounds.
-
Materials Science: Understanding lattice energy is essential for designing new materials with specific properties, such as high melting points, hardness, and electrical conductivity.
Related Searches: Expanding the Knowledge Base
Exploring lattice energy trends leads to a deeper understanding of related concepts and applications. Here are some related searches that offer valuable insights:
-
Born-Haber Cycle: This thermodynamic cycle allows for the calculation of lattice energy from experimentally determined enthalpy changes of other reactions.
-
Kapustinskii Equation: This empirical equation provides an approximate value for lattice energy based on the charges and radii of the ions.
-
Ionic Radius Trends: Understanding ionic radius trends is essential for predicting lattice energy variations across the periodic table.
-
Enthalpy of Formation: This thermodynamic quantity relates to the energy change involved in forming one mole of a compound from its constituent elements in their standard states.
-
Solubility Rules: These rules predict the solubility of ionic compounds based on the lattice energy and other factors.
-
Crystal Structures: Understanding different crystal structures helps predict the arrangement of ions and their impact on lattice energy.
-
Electrostatic Interactions: Lattice energy is directly related to the strength of electrostatic interactions between ions in the crystal lattice.
-
Bond Energies: While lattice energy focuses on ionic compounds, bond energies relate to the strength of covalent bonds in molecules.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Queries
Q1: How is lattice energy measured experimentally?
Lattice energy cannot be directly measured experimentally due to the difficulty of isolating individual ions in the gaseous phase. However, it can be calculated using the Born-Haber cycle, which combines enthalpy changes of other experimentally measurable reactions.
Q2: How does lattice energy affect the melting point of ionic compounds?
Compounds with higher lattice energy generally have higher melting points. This is because more energy is required to overcome the strong electrostatic forces holding the ions together in the crystal lattice.
Q3: Can lattice energy be negative?
Lattice energy is always a positive value because it represents the energy released when ions come together to form a crystal lattice.
Q4: How does lattice energy relate to the solubility of ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds with high lattice energy tend to be less soluble in water because the strong electrostatic interactions within the crystal lattice are difficult to overcome by the water molecules.
Q5: How does lattice energy affect the reactivity of ionic compounds?
Compounds with high lattice energy are generally less reactive due to the strong ionic bonds holding the ions together.
Tips for Understanding Lattice Energy Trends
-
Visualize the periodic table: Use the periodic table as a visual aid to understand the trends in ionic charge and size, which directly affect lattice energy.
-
Focus on the key factors: Remember that ionic charge and size are the primary determinants of lattice energy.
-
Consider the exceptions: There are exceptions to the general trends in lattice energy, so it’s essential to consider other factors, such as crystal structure and polarizability.
-
Practice with examples: Work through examples of ionic compounds to solidify your understanding of lattice energy trends and their applications.
Conclusion: Illuminating the Importance of Lattice Energy
Lattice energy is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides valuable insights into the properties and behavior of ionic compounds. By understanding the trends in lattice energy across the periodic table and its influence on various chemical phenomena, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay of forces that govern the world around us. From predicting solubility and reactivity to designing new materials, the concept of lattice energy continues to be a cornerstone of chemical understanding and innovation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Secrets of Lattice Energy: A Journey Across the Periodic Table. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!