Visualizing the Future: The Power of Graphs in Tracking Trends Over Time
Visualizing the Future: The Power of Graphs in Tracking Trends Over Time
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Visualizing the Future: The Power of Graphs in Tracking Trends Over Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing the Future: The Power of Graphs in Tracking Trends Over Time

The ability to understand and predict future trends is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike. While the future is inherently uncertain, data analysis and visualization offer powerful tools for discerning patterns and making informed decisions. Among these tools, graphs that show trends over time play a pivotal role in revealing the trajectory of various factors and providing valuable insights into potential outcomes.
Understanding the Power of Time-Series Graphs
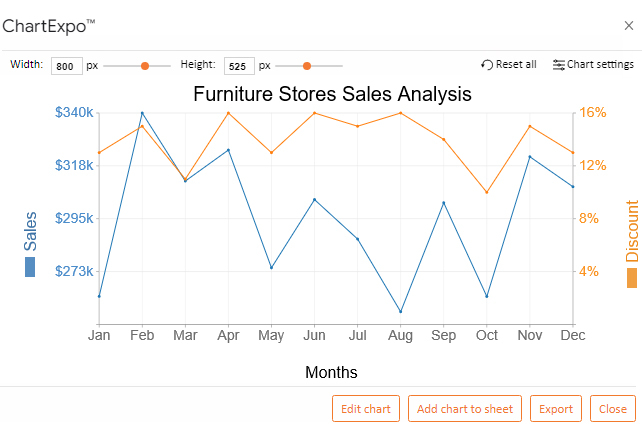
Time-series graphs, also known as line graphs, depict data points collected over a specific period. They connect these data points with lines, creating a visual representation of how a particular variable changes over time. This visual representation offers several advantages:
- Identifying Patterns: Time-series graphs allow for the identification of trends, seasonality, and cyclical patterns within data. This helps in understanding the underlying forces driving change and predicting future behavior.
- Visualizing Growth and Decline: The slope of the lines in a time-series graph indicates the rate of change. A steep upward slope suggests rapid growth, while a downward slope indicates decline. This information is crucial for making informed decisions about resource allocation and strategy.
- Comparing Trends: Time-series graphs can be used to compare different trends simultaneously. This allows for analyzing relationships between variables, identifying correlations, and understanding how different factors influence each other.
- Communicating Complex Data: Visual representations like time-series graphs are highly effective in communicating complex data to a wide audience. They make it easier to grasp trends and patterns compared to raw data tables.
Applications of Time-Series Graphs in Diverse Fields
The applications of graphs that show trends over time are vast and extend across numerous disciplines:
- Business: Businesses use time-series graphs to track sales figures, customer acquisition rates, marketing campaign performance, and stock prices. This data helps in identifying growth opportunities, optimizing strategies, and making informed decisions regarding investments and resource allocation.
- Finance: Financial analysts rely heavily on time-series graphs to analyze stock market trends, track bond yields, and assess economic indicators. These graphs provide crucial insights for investment strategies, risk management, and portfolio optimization.
- Healthcare: Time-series graphs are used to monitor patient health metrics like blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels. These graphs help healthcare professionals identify potential health issues, track treatment effectiveness, and adjust care plans accordingly.
- Environment: Scientists use time-series graphs to analyze climate data, track greenhouse gas emissions, and monitor changes in biodiversity. This data informs environmental policy decisions, conservation efforts, and sustainable development strategies.
- Social Sciences: Researchers in sociology, psychology, and political science use time-series graphs to study demographic trends, social movements, and political behavior. These graphs help understand social change, identify potential social issues, and inform policy interventions.
Delving Deeper into Related Searches
To further explore the potential of graphs that show trends over time, let’s delve into eight related searches that offer valuable insights into specific applications and techniques:
1. Time Series Analysis: This search leads to a deeper understanding of the statistical methods used for analyzing time-series data. It encompasses techniques for identifying patterns, forecasting future values, and understanding the underlying processes driving change.
2. Time Series Forecasting: This search focuses on predicting future values based on historical data. It explores various forecasting models, including ARIMA, exponential smoothing, and machine learning algorithms, which are used to project future trends.
3. Trend Analysis: This search delves into the methods for identifying and interpreting trends within time-series data. It covers techniques for recognizing upward and downward trends, seasonal fluctuations, and cyclical patterns.
4. Time Series Decomposition: This search explores the process of breaking down a time-series into its constituent components, such as trend, seasonality, and noise. This decomposition helps isolate the individual components and analyze their impact on the overall trend.
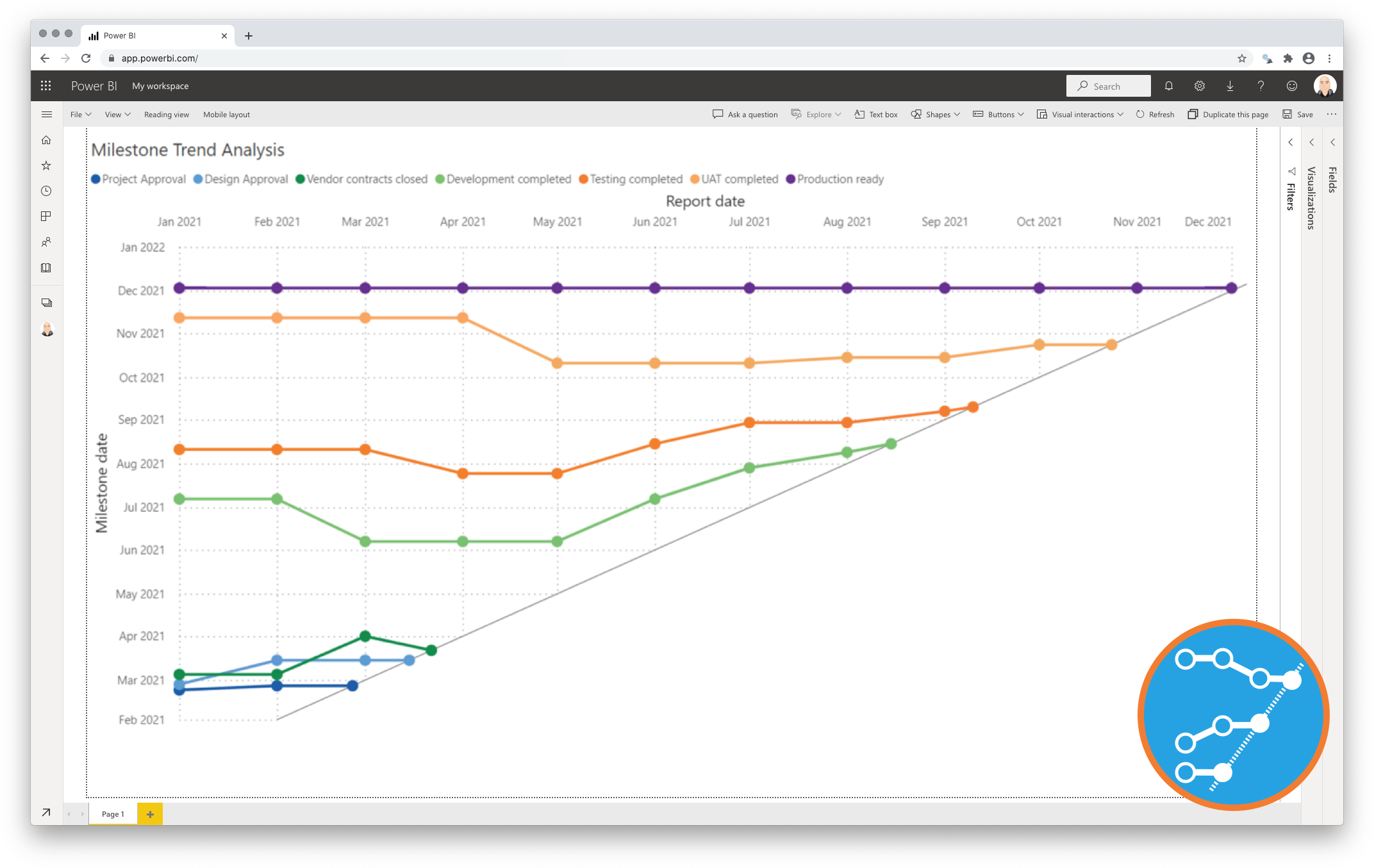
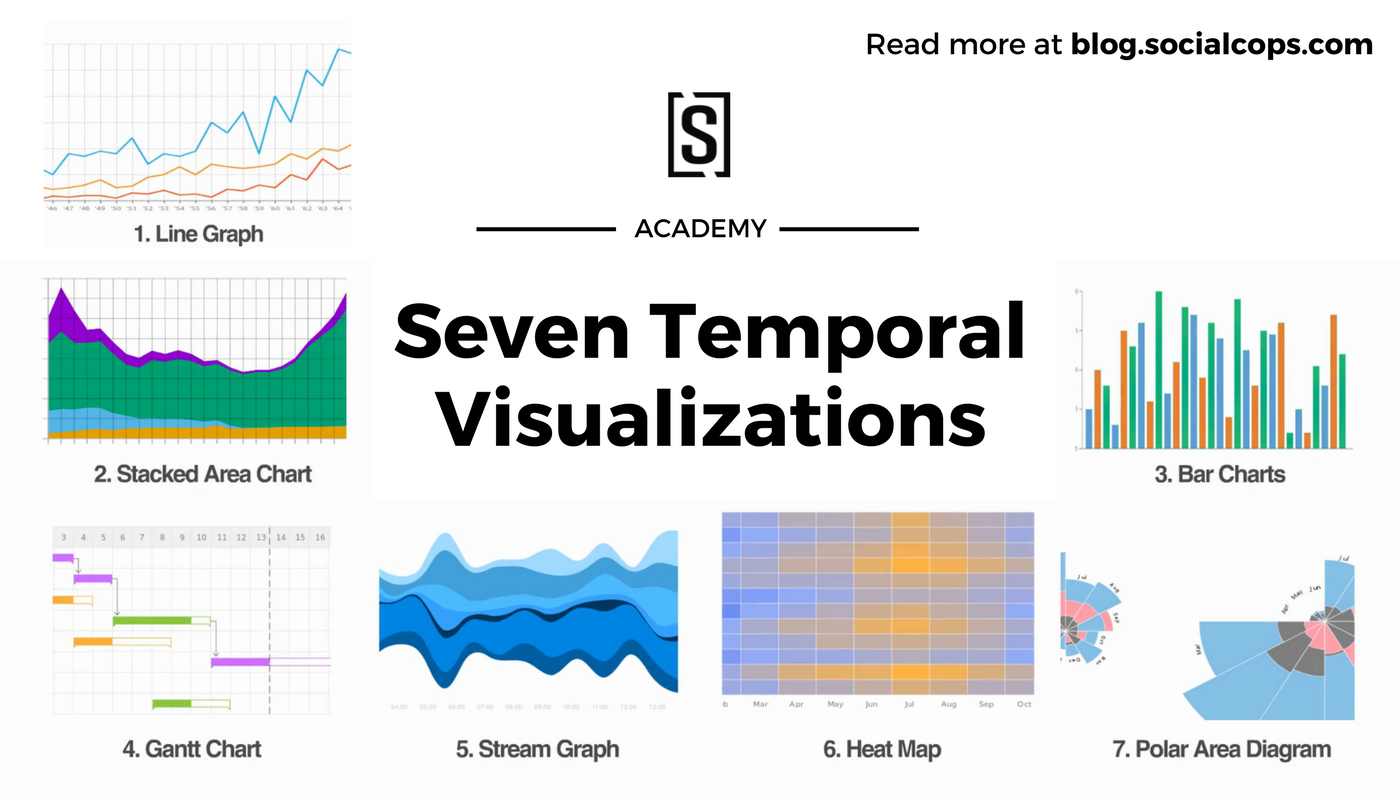
5. Time Series Visualization: This search focuses on the various techniques and tools used to visualize time-series data effectively. It explores different types of graphs, including line charts, bar charts, and scatter plots, and their specific applications.
6. Time Series Data in R: This search explores the use of the R programming language for analyzing and visualizing time-series data. R offers a wide range of packages and functions specifically designed for time-series analysis.
7. Time Series Data in Python: This search focuses on the use of Python for time-series analysis. Python libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn provide powerful tools for working with time-series data.
8. Time Series Data in Excel: This search explores the use of Microsoft Excel for basic time-series analysis. Excel offers built-in functions and charting tools that can be used for simple trend analysis and visualization.
Addressing Common Questions
FAQs about Graphs that Show Trends Over Time
1. What are the different types of time-series graphs?
There are several types of time-series graphs, each with its own strengths and applications:
- Line charts: The most common type, used to visualize trends and changes over time.
- Area charts: Similar to line charts, but the area beneath the line is filled, highlighting the magnitude of change.
- Bar charts: Used to compare values across different time periods, particularly helpful for visualizing discrete data points.
- Scatter plots: Used to visualize relationships between two variables over time, revealing correlations and patterns.
2. How do I choose the right type of time-series graph?
The choice of graph depends on the specific data and the message you want to convey. Consider factors like the type of data, the number of variables, and the desired level of detail.
3. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating time-series graphs?
Common mistakes include:
- Using an inappropriate scale: Ensure the scale accurately reflects the data range and avoids distortion.
- Overcrowding the graph: Avoid cluttering the graph with too much information.
- Choosing an unclear color scheme: Opt for a clear and contrasting color scheme for easy readability.
- Lacking context: Provide clear labels, titles, and legends to provide context for the data.
4. How can I use time-series graphs for forecasting?
Time-series graphs can be used for forecasting by identifying trends and patterns in historical data. This information can be used to extrapolate future values, though it’s important to remember that forecasts are based on assumptions and may not always be accurate.
5. What are the limitations of time-series graphs?
While powerful, time-series graphs have limitations:
- Data quality: The accuracy of the graph depends on the quality of the underlying data.
- External factors: Time-series graphs may not capture all the external factors that could influence trends.
- Causality: Correlation does not imply causation. A strong trend does not necessarily mean one variable causes the other.
Tips for Effective Time-Series Graph Creation
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the graph and what you want to communicate.
- Choose the right data: Select relevant and accurate data for your analysis.
- Select an appropriate graph type: Choose the type of graph that best represents the data and your objective.
- Use clear and concise labels: Ensure labels, titles, and legends are clear and easy to understand.
- Choose a visually appealing color scheme: Opt for a color scheme that enhances readability and visual impact.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding the graph with too much information.
- Provide context: Include relevant background information to help viewers understand the data.
- Use tools for data analysis and visualization: Utilize software like Excel, R, or Python to create effective graphs.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Time-Series Graphs
Graphs that show trends over time are invaluable tools for understanding the past, analyzing the present, and predicting the future. They provide a visual representation of change, revealing patterns, identifying correlations, and facilitating informed decision-making. By mastering the creation and interpretation of these graphs, individuals and organizations can leverage the power of data visualization to navigate a complex and ever-changing world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing the Future: The Power of Graphs in Tracking Trends Over Time. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!